The products and services section of your business plan is much more than a list of products or services you will offer.
It includes a detailed description of the problem you solve, the pricing you charge, and the intellectual properties you own. Moreover, it also offers insight into your marketing and order fulfillment process.
Well, that’s not it.
There’s a lot more to the products and services in a business plan and we shall discuss that in this blog post. Also, we will share a few creative tips to make this section informative.
So, let’s get started.
Key Takeaways
- This section describes the products or services your business offers, highlighting their value to customers.
- It should detail features, benefits, pricing, and the unique selling proposition of each offering.
- Including information on product lifecycle, research and development, and future offerings adds depth.
- Demonstrating how your products or services meet market needs strengthens your business plan.
What is the products and services section?
The products and services section of your business plan is where you mention and elaborate on your product range, product descriptions, pricing strategies, and other relevant details.
If you’re looking for partners or investors, this section plays a crucial role in persuading them. What you include in this section and how you write it can deeply impact whether or not your investors will seal the deal with you.
What to include in the products and services section?
The products and services section is the most important component when you write your business plan.
It includes everything a prospective reader needs to understand the products you sell—its unique selling proposition (USP), pricing, marketing tactics, delivery, and order fulfillment process. In short, a complete detailed guide about your business’s product and services.
Let’s explore this section in more detail as we dive further.
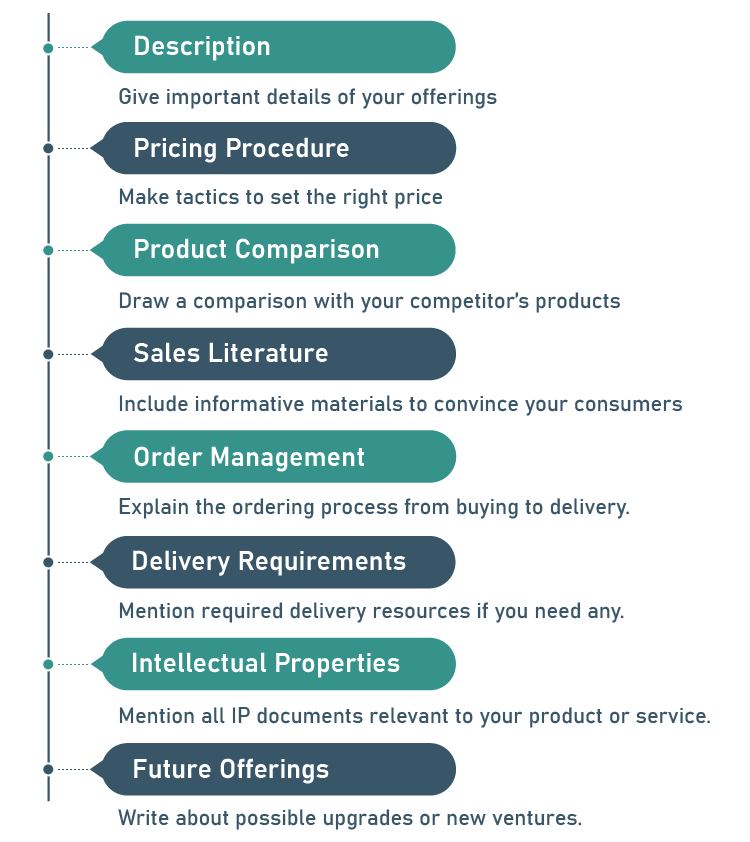
1. Description
In this part, include all the important details of your offerings. To write an accurate description, use the 5W2H(who, what, when, where, why, how and how much) method and answer these questions:
- Who can use this product? Mention the details of your ideal customer.
- What are the fundamental aspects of your product? These may include features, materials, ingredients, costs, dimensions, etc.
- When should someone use this product? Mention the occasion, or the season if it’s a seasonal product. You can also mention if it’s designed for a specific purpose.
- Where should your customers use the product? Is it used indoors or outdoors? Specify these details.
- Why should your customers use your product? Mention how the product fulfills their needs.
- How should they use your product? Mention if there are any important user instructions.
- How much should they use it? Mention the ideal frequency of usage that’s essential to follow while using your product.
2. Pricing procedure
A pricing strategy refers to the tactics you use to set a price for your products and services. While there are various strategies to choose from, conducting a price analysis will help you determine the pricing strategy that works best for your business model.
Follow this step-by-step procedure to conduct a pricing analysis:
Determine cost of goods sold (COGS)
To calculate the total cost of your products and services, add all the expenses that you incurred before the sale. This will include costs such as manufacturing, labor, warehousing, distributing, packaging and labeling, marketing, etc.
Also, determine your profit markup and add that to the COGS to set the final price for your products.
Collect data about the price preferences of your customers
Study your target customer’s opinions regarding pricing through surveys and questionnaires. This helps you know your customers’ price sensitivity.
Using this data, you can set an equilibrium price that’s low enough to sustain demand and high enough to secure profits.
Study your competitors’ prices
Perhaps the best way to tell whether a price works is by looking at the prices of your direct competitors.
Direct competitors are those who sell the same products as you do. Analyzing their pricing strategy helps you understand the price range for similar products in the current market.
With this information, you can modify your prices to set a competitive price.
Consider all the legal and ethical aspects
Setting a price that induces sales is essential.
However, ensure that you don’t set a price so low that it cuts off the competition. Such practice, often regarded as predatory pricing, is considered illegal in certain industries.
To avoid such troubles, be aware of the laws applicable to your business.
After conducting a pricing analysis, you can look at these pricing strategies to choose one for your business.
3. Product comparison
Regardless of what you’re selling, someone in the market might already be selling it. Unlike direct competitors, indirect competitors sell similar products with slight variations.
Looking at your competitors can help you draw a comparison. To do that, examine their products and services and list down the similarities and differences.
Categorize this information into qualitative and quantitative aspects and organize it in tables. Finally, summarize it by including your advantages over competitors. Also, include how you will leverage them to balance your drawbacks.
4. Sales literature
Sales literature refers to the promotional and informative materials you use to inform, clarify, and convince your customers to make buying decisions. These include brochures, catalogs, newsletters, price lists, customer testimonials, and case studies.
List out all the sales literature you use to market your products and services and briefly outline the information it conveys. Another integral part of your sales literature is your website; explain how it contributes to your sales.
Perhaps you run a blog to promote your products and inform your customers about new releases. Maybe you sell your products and services directly from your website; in that case, your sales literature material will go there.
5. Order management
From the moment a customer places an order to the delivery, followed by after-sales services—order processing constitutes everything.
Here, you explain how customers will order or buy the products and detail your delivery process.
For instance, for an online retail store, the order processing may include stages like:
- Order placement
- Order processing
- Picking inventory
- Sorting
- Packing
- Shipping
- Product delivery
- Customer support
- Returns
Depending on your offerings, your order processing workflow can have several stages. Describe each step and provide elaborate details about the execution.
6. Delivery requirements
If the delivery or creation of your products and services needs any resources, mention them here. These can include equipment, vehicles, technology, and software.
For instance, a cafe owner will need kitchen equipment and IT solutions to run and provide its services. Mention these things in this part of the products and services section.
To cite another example, a consumer electronics company needs an IT infrastructure and production facility to create its products. For delivery, it needs vehicles and an online portal for customers to place and receive orders. All these are mentioned here.
7. Intellectual properties
Mention all the Intellectual Property (IP) documents that are related to your products and services. These include trademarks, seller permits, patents, other licenses, etc.
Here you can also include any legal issues you’re currently facing and explain how you’re dealing with them.
Further, mention the issues that might occur in the future and the counteractive measures you will take to prevent them. These include adding safety labels, and disclaimers, opting for insurance policies, etc.
8. Future offerings
This is a chance to impress your investors or partners by briefing them about your future products or services.
If your future products are an extension of the current products, offer an outline of the improvements you will make and clarify if the products are under development or ready for launch.
You can alter the products and services section as you wish to fit your product ideas the best. However, we have some practical tips that can help you make this section enriching.
6 Tips on writing a good products and services section

Bear these tips for the business plans products and services section in mind when you start writing. Remember, this is just a list. You can always find other little tactics most unique to your product, service or industry.
1. Opt for a customer-centric approach
Your goal is to cater to the needs of your customers through your products or services. Hence, write as if you’re talking to your customers and directly addressing their issues. Point out how your product will make their lives better and easier.
2. Keep it simple
Clearly represent the information. Use bullet points and lists to convey your message. You can also use tables and charts to display product comparisons, strengths, etc.
3. Ditch buzzwords and industrial jargon
Everyone who reads your business plan may not understand the industrial jargon and buzzwords. Therefore, it’s best to skip the complicated lingo and use layman’s terms.
4. Specify market pain points
Elaborate on the problems your target audience is facing. You can gather this data by conducting a market analysis. Mention the various pain points and the features of your product that address them. Consider citing examples and relevant statistics to display how your product solves a customer problem.
5. Emphasize your USP
Highlight the benefits and the unique features of your products and services. Mention the things you do differently than your competitors and how you offer more value in comparison.
6. Flaunt your achievements
Make sure to show off the business milestones you’ve achieved such as awards, news articles, customer reviews, etc. You can also include your past sales numbers, your customer base, and the projects you fulfilled. These instill trust and help potential investors, clients, and partners to make decisions.
Persuade interest with a product and service section
Your products and services are the lifeblood of your business. Its accurate representation in a business plan is essential to instill investors’ faith in your ability to achieve growth and secure funding.
Ensure that this section communicates the value of your product offerings and highlights your strategies to market, sell, and deliver customer orders.
Now, kickstart writing this section. However, remember that you need to complete other sections of your business plan, as well.
Using a business planning app like Upmetrics could be a smart choice to streamline your entire plan writing process. Its AI business plan generator uses the information you offer to create detailed plans in less than just 10 minutes.