Ever notice how Blockbuster (former giant video rental chain) looked unstoppable in the 2000s?
Stores everywhere, millions of customers, strong profits. But outside forces, like faster internet and new tech, changed the game. Netflix spotted it; Blockbuster didn’t. And we all know how that story ended.
That’s why I swear by PESTEL analysis. It’s like putting on wide-angle glasses: you see political, economic, social, tech, environmental, and legal shifts before they hit your business.
As an entrepreneur myself, I’ve seen other entrepreneurs skip this step and pay the price later. The good news? Doing it is simple.
In this post, I’ll show you how to run a PESTEL analysis step by step—with examples—so you can future-proof your business strategy.
What is a PESTEL analysis? (And what it’s used for)
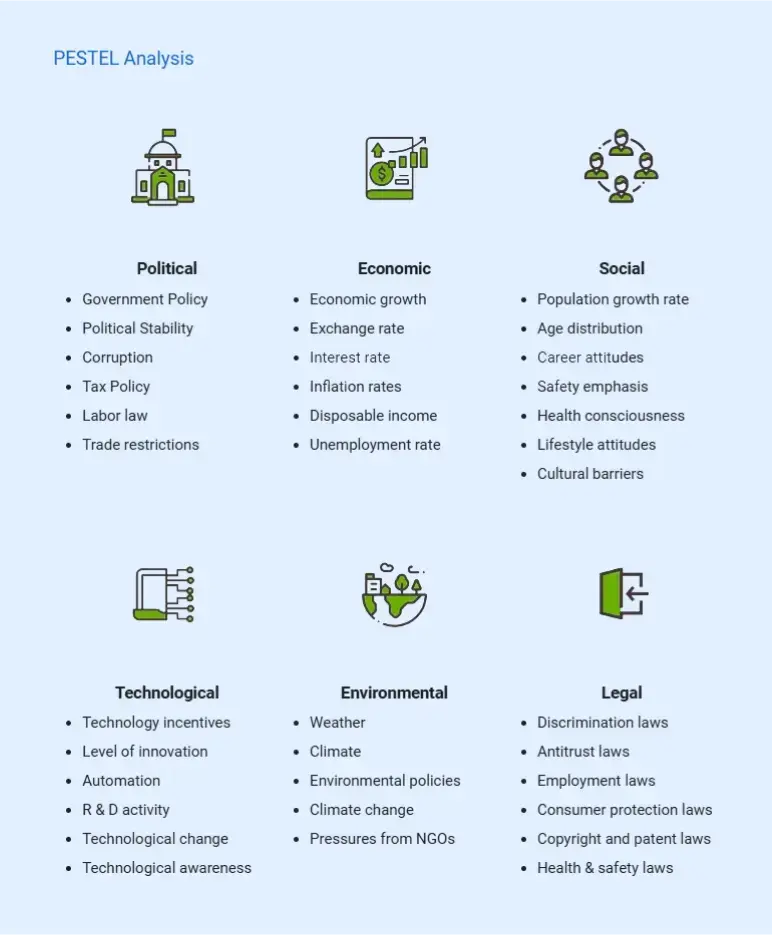
A PESTEL analysis is a structured framework that helps you scan the outside world for forces that could shape your business. Instead of only looking inward, you check six big areas:
- Political: Government stability, policy changes, trade agreements, taxes.
- Economic: Interest rates, inflation, consumer spending, growth trends.
- Social: Shifts in culture, demographics, or customer behavior.
- Technological: Innovation, automation, new tools, or infrastructure.
- Environmental: Climate issues, sustainability expectations, or environmental policies.
- Legal: Regulations, compliance rules, and intellectual property laws.
PESTEL analysis helps teams spot opportunities and risks that are easy to overlook because they’re outside the company’s direct control. When paired with an industry analysis, it gives a complete picture.
For example, a fintech startup preparing a national launch might realize that new compliance rules could slow expansion. A founder building an investor-ready plan could point to regulatory changes or rapid shifts in technology to show they’ve considered external risks, something investors value.
And a retailer planning for a downturn might use PESTEL to map how inflation and weaker consumer spending could affect pricing, hiring, or expansion decisions.
Understanding the categories is easy. Using them to uncover real opportunities and risks takes a bit more care. Let’s see how to do a PESTEL analysis the right way.
→ Download Now: Market Analysis Kit
How to conduct a PESTEL analysis: step-by-step process
A PESTEL analysis works best when you connect it to a specific decision, not just as a general “let’s see what’s out there” exercise. Basically, my point is, if you don’t start with a clear focus, you’ll end up with a messy list of factors and no idea what to actually do with them.
Here’s a step-by-step process to do it:
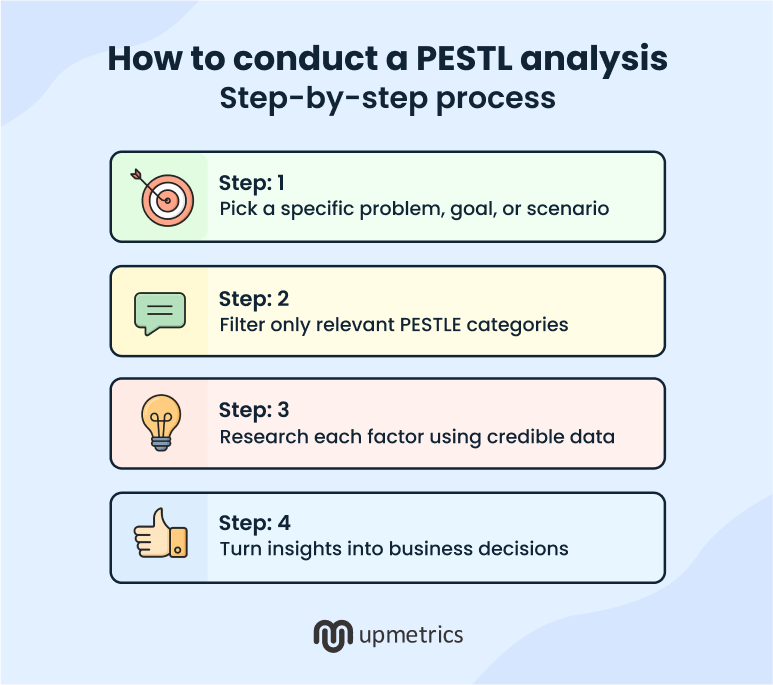
Step 1: Pick a specific problem, goal, or scenario
Start by getting clear on what you’re analyzing. Don’t try to “PESTEL the whole business” in one go; it’ll only give you a long list of random factors you can’t act on.
Instead, focus on one situation: maybe you’re planning a new market launch, adjusting pricing for the next year, or raising funds and need to show investors you’ve thought about external risks.
Once you have that focus, begin with the political side. Look at things like government stability, tax changes, trade restrictions, tariffs, labor laws, or new regulations that could impact your plans.
These issues have real costs. U.S. small businesses spend about $14,700 per employee every year on regulatory compliance, which is 20% more than larger firms (NAM report). If you’re not accounting for those costs upfront, your forecasts will almost always come in short.
And if you’re working across countries, ensure to scan both local and international policies. Here’s a real example:
A fintech startup I know was ready for a national rollout. The real risk wasn’t their tech; it was a set of compliance rules that could’ve delayed their launch by six months. Because they caught that early, they were able to adjust the roadmap, set aside budget for legal work, and avoid a last-minute scramble.
The main idea here: Be specific. Define the exact situation you’re analyzing and the external forces that could shift the outcome. That clarity makes the rest of the process faster and way more useful.
Step 2: Filter only relevant PESTEL categories
A mistake I see often is giving each of the six categories equal weight, even when half don’t apply. That’s how teams get buried in details that don’t actually matter.
In my experience, PESTEL works best when treated like a funnel, starting broad, then narrowing in on the factors that truly affect your business.
Start wide by looking at all six areas, then narrow in on the few that could actually influence the goal or decision being worked on. In other words, focus on the forces that could realistically change the timeline, budget, or strategy.
Here’s a simple way to filter them:
- Political: Will regulations or policy shifts directly affect how the business operates or launches?
- Economic: Could changes in interest rates, inflation, or consumer spending patterns affect sales or costs?
- Social: Are shifts in customer values, habits, or demographics likely to change demand?
- Technological: Is the product tied to tech trends that could speed growth or make it obsolete overnight?
- Legal: Are there new laws on data, employment, or product compliance that need to be met?
- Environmental: Could climate, geography, or sustainability expectations affect operations or reputation?
The fewer distractions you have, the easier it is to spot the factors that could make or break your plan
Step 3: Research each factor using credible data
A PESTEL analysis without solid data will crumble the moment it’s challenged, and it will be challenged. Investors, board members, and even your own team will ask, “Where did this insight come from?”
The way to avoid that is to treat each factor like a mini research project. You don’t need every number available, just evidence from sources people trust.
Political factors often come from government policy sites or industry reports. Economic trends might be grounded in World Bank data, central bank updates, or labor statistics. Social shifts can be backed by research centers or census data.
For technology, think Gartner reports or adoption studies. Legal and environmental insights are often found in regulatory updates, compliance notices, or climate guidelines.
Handled this way, PESTEL becomes something you can actually defend in a pitch or planning session. Even more importantly, these insights feed directly into your market analysis, strengthening forecasts and showing that your assumptions are backed by real-world signals.
Step 4: Turn insights into business decisions
A PESTEL analysis has no real value if it ends as a slide full of bullet points. The real win is turning “things we know” into “things we’ll do.”
The easiest way to do that? Ask “So what?” after every insight. For example:
- There’s a new data law coming. So what? → Revise the onboarding flow to collect consent.
- Inflation is trending up. So what? → Revisit pricing before next quarter.
- A competitor is rolling out an AI feature. So what? → Test a rapid prototype for AI integration.
Here’s a quick structure I recommend:
| Factor | Insight | Risk/Opportunity | Action |
|---|---|---|---|
| [Political/ Economic/etc.] | [Write the external factor here] | [Decide if it’s a risk or opportunity] | [Define the business action you’ll take] |
That’s the structure. Now let’s see it filled out with a real example so you can understand how it works in practice.
Imagine you’re running a mid-sized food delivery startup. You’ve just wrapped up your PESTEL analysis, and here’s what comes up:
| Factor | Insight | Risk/Opportunity | Action |
|---|---|---|---|
| Political | City council pushing stricter traffic laws for delivery bikes | Risk | Shift deliveries to e-bikes and update vendor contracts, resulting in less noise. |
| Economic | Rising fuel prices are squeezing margins | Risk | Add a small fuel surcharge to delivery fees. |
| Social | Surge in demand for healthier food options | Opportunity | Partner with salad chains and launch campaigns like “Healthy Mondays”. |
| Tech | Competitors are adding real-time order tracking | Opportunity | Fast-track a live tracker so customers can watch their order status in real time. |
| Legal | New labor law requiring better rider benefits | Risk | Redesign rider contracts and budget for compliance. |
| Environmental | Push for eco-friendly packaging | Opportunity | Pilot biodegradable containers. |
To an investor, “rising fuel prices” or “new labor laws” aren’t just external factors; they’re proof you’ve thought ahead. PESTEL helps you turn those forces into clear actions, making your plan more credible and grounded.
Bottomline? By the time you’ve worked through this step, you’ll have a PESTEL and a roadmap that tells your team exactly how to respond to the world outside your walls.
Ready to try it yourself? In the Upmetrics app, you can view a PESTEL analysis template and even get AI guidance to fill it out. It will look something like this:
How to include PESTEL analysis in a business plan or pitch deck?
On its own, a PESTEL analysis is just research. The real value comes when you weave those insights into the bigger story you’re telling, whether it’s for investors, lenders, or strategic partners.
Most investors won’t ask, “Can you show me your PESTEL analysis?” What they will expect is proof that you understand the outside forces that could speed up or slow down your business and that you’ve already planned for them.
Here’s where it fits best in a business plan or deck:
In the market analysis section
In the market analysis sections, PESTEL findings give your numbers context. A favorable policy change (political) or a surge in adoption rates (technological) can show why now is the right time to enter the market.
In the risk section
Highlight relevant threats and show you have a mitigation plan. If there’s an upcoming regulation (legal) or shifting consumer trend (social), pair it with the steps you’ll take to address it.
In the strategy section
A strategy backed by outside context is far more convincing than a list of tactics. If your technological scan shows the industry is moving fast toward AI, your roadmap, partnerships, or pricing should reflect that shift. If your social analysis shows one demographic is adopting faster than others, highlight why they’re your focus.
In your financials
External factors influence your numbers. If economic analysis points to rising inflation, show how you’ve factored potential cost increases into projections. If environmental policies could raise compliance costs, build them into your forecast.
Another use is less obvious but equally important: Feeding your PESTEL findings into other tools and planning sections. For example:
- Risk mitigation plans
- Go-to-market timelines
- Regulatory barrier explanations
- Scenario planning for expansion or downturns
The point is: Don’t treat PESTEL as a separate report. Use it as a lens across your plan so anyone reading can see you’ve thought about the world outside your product vision.
Some teams also connect PESTEL with a SWOT analysis, but the bigger win is weaving those insights directly into the core sections of your business plan.
Conclusion
Too often, founders treat PESTEL like a checkbox exercise—add a few bullet points to the appendix and move on.
But the businesses that last are the ones that keep this lens alive. Investors expect it too: Deloitte reports that 80% of institutional investors use sustainability data in their decisions. That shows how much weight they place on external factors.
The key isn’t just listing PESTEL categories; it’s connecting them to your strategy and financials. And that’s easier when you’re using the right tool.
With Upmetrics, you can map external factors, link them to milestones and forecasts, and keep them visible as your plan evolves, instead of leaving them buried in an appendix.


