Executive Summary
SkillForge Technical Vocational Institute, LLC is a new training school in Columbia, South Carolina, offering hands-on programs in HVAC, electrical technology, welding, medical assisting, and automotive service. The campus will include fully equipped technical labs, classrooms, and safety systems needed for practical instruction.
This plan supports a request for a state workforce development grant and a TD Bank education loan to build out the facility, install lab equipment, hire instructors, and complete licensing.
SkillForge will train adults, recent graduates, and veterans for steady technical jobs in the Columbia metro area, helping local employers fill long-standing shortages in skilled trades and entry-level medical roles.
Employers report ongoing vacancies, while existing schools such as Midlands Technical College and smaller career institutes operate with limited seats, rigid schedules, and recurring waitlists.
These conditions create a direct opening for SkillForge. The unmet demand creates room for a school that offers flexible cohorts, short programs, and modern labs. SkillForge can absorb overflow applicants, support adults who cannot enter waitlisted programs, and supply employers with technicians that the current system cannot produce fast enough.
Potential Clients
SkillForge will primarily serve:
- Adults seeking a career change or skills upgrade without pursuing a four-year degree
- Recent high school graduates in the Columbia area who prefer job-focused training
- Veterans and dislocated workers referred through state workforce programs
By concentrating on these groups, SkillForge aims to maintain steady cohorts of motivated students and help reduce shortages in HVAC, electrical, welding, medical assisting, and automotive service roles.
Key Owners
Dr. Elaine Porter (70 %) is the founder and Campus Director. She possesses more than 18 years of experience in leadership in vocational education and once worked as a dean at Midlands Technical College, where she contributed to the design of HVAC and electrical programs.
The Workforce Partnerships Director is Michael Reyes (20 %). With the South Carolina Department of Employment and Workforce, he has had previous experience in establishing contact with the employers who employ technicians.
Jasmine Calder (10 %) holds the position of Academic Program Lead. Her curriculum development and lab education background are present.
Collectively, the ownership team has a background in campus operations, workforce relationships, and technical training. Through specialized startup investment, systematic program implementation, and employer feedback, SkillForge will provide steady streams of work-ready graduates that advance labor in the area.
Financial Highlights
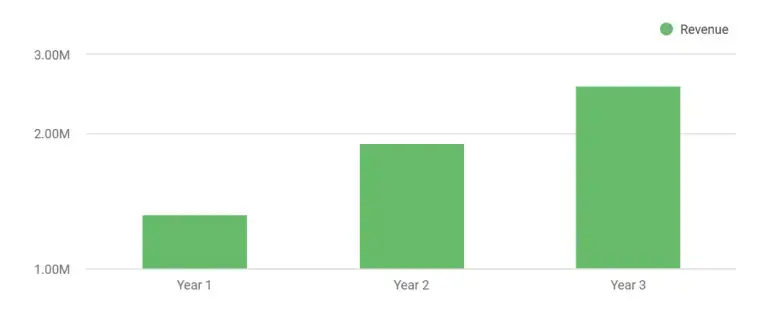
SkillForge will launch with five programs and gradually scale enrollment. A realistic Year 1 intake is 110–125 students. With an average tuition of about $11,000 per student, Year 1 revenue is estimated at $1.2–$1.35 million. The school will still post a planned first-year loss due to payroll, marketing, and lab setup required during the startup phase.
By Year 2, referral flow and marketing performance should be more stable, and enrollment is projected at about 160–180 students, with revenue of roughly $1.75–$2.05 million. At this level, the school is expected to post its first profitable year, assuming disciplined cost control and solid retention.
In Year 3, with mature cohorts and stronger employer ties, enrollment is expected to reach approximately 210–240 students. Revenue in this scenario is projected at $2.3–$2.7 million, with margins sufficient to cover loan payments and build reserves.
Funding Requirement
SkillForge is requesting a total of $1.25 million to launch the Columbia campus. This includes a $420,000 state workforce development grant, a $650,000 education loan from TD Bank, and $180,000 in owner equity. These funds cover facility buildout, lab equipment, software, licensing, early payroll, and a working capital buffer for the first several months of operations.
Total startup funding will be $1.25 million, which covers identified startup costs and provides working capital for the launch period.
Want a professional plan like this sample?
Upmetrics AI generate a complete, investor-ready plan for you

Business Overview
SkillForge Technical Vocational Institute is a registered company in South Carolina as a Limited Liability Company. This form helps in multi-owner management, compliance by lenders, and accreditation in the future.
The school will commence its operation with the state authorization of the South Carolina Commission on Higher Education, as well as fire and safety inspections of the HVAC, welding, and electrical laboratories of the school.
There are five certification programs at SkillForge: the HVAC, electrical technology, welding, medical assisting, and automotive service. These programs have been chosen since they fit the confirmed workforce gaps in the Columbian metro region and do not require prolonged academic processes, but practical studies. All programs are structured 610-month-long that fit working adults, new graduates, and veterans.
The campus will be housed in a leaseable facility at 1420 Midlands Innovation Drive, which is located in the BullStreet district. The building accommodates intensive technical education and has the necessary teaching facilities.
Campus Features
- Five dedicated labs (HVAC, electrical, welding, medical assisting, automotive)
- Two classrooms and a computer lab
- Admissions, faculty, and career services offices
- Storage for tools, PPE, and consumables
- Upgraded ventilation, electrical load capacity, and safety systems
- Transit access and visibility for adult learners
SkillForge’s mission is to provide technical training that leads directly to stable employment. Its vision is to become a dependable South Carolina training provider that supplies employers with steady cohorts of certified entry-level technicians.
Ownership & Management
The institute is owned and managed by three members who combine vocational education experience, workforce agency insight, and technical curriculum expertise. Their roles focus on academic quality, employer coordination, and operational compliance.
| Owner | Ownership % | Title | Primary Responsibilities |
|---|---|---|---|
| Dr. Elaine Porter | 70% | Managing Member / Campus Director | Oversees campus operations, instructor management, program quality, and licensing |
| Michael Reyes | 20% | Managing Member / Workforce Partnerships Director | Manages employer relationships, referral pipelines, and placement channels |
| Jasmine Calder | 10% | Academic Program Lead | Oversees curriculum, lab procedures, and student performance systems |
This leadership team provides the operational and academic foundation required for SkillForge to deliver consistent outcomes, manage regulatory requirements, and build long-term employer partnerships.
Advisory & Support Resources
SkillForge will collaborate with the already established partners to support the quality of training, safety, and regulation.
- Accreditation Standards: Accrediting Council of Continuing Education and Training (ACCET) standards.
- Staffing: South Carolina Department of Employment and Workforce
- Safety and lab compliance: OSHA regulations on welding, HVAC, and electrical labs
- Accounting and financial reporting: Certified accountant with experience in the education sector compliance
- Equipment vendors: Miller Electric, Snap-on, Fluke, Trane, MedLab USA
These partners provide program development support, safety oversight, and financial compliance.
Business Goals
- Establish a well-equipped first campus with consistent student outcomes
- Reach a stable enrollment of 200–250 students within five years
- Secure ACCET accreditation and prepare for GI Bill approval
- Strengthen job placement partnerships across local employers
- Offer day, evening, and weekend cohorts
- Develop a second campus once the Columbia site reaches full capacity
- Maintain safe labs, clear training standards, and strong student support systems
These goals position SkillForge as a reliable contributor to South Carolina’s workforce pipeline.
Market Research
National Outlook
Demand for skilled trades continues to rise across the United States because of retirements and industry growth.
According to the U.S. Bureau of Labor Statistics, HVAC technicians are expected to grow 8% from 2024–34, and medical assistant roles are projected to grow 12%; both faster than average. Many installation, maintenance, and repair occupations (including trade and auto-service roles) are forecast to grow faster than average overall, pointing to steady demand for skilled-labor training.
South Carolina & Columbia Region
South Carolina continues to report shortages across HVAC, welding, electrical, medical assisting, and automotive roles. Labor data for the Columbia area shows consistent vacancies in these fields, and several remain listed as “hard-to-fill.”
Opportunity for SkillForge
SkillForge fills a clear training gap in Columbia, South Carolina. The region needs more capacity, more flexible schedules, and more labs using industry tools. By offering short 6–10 month programs, day and evening cohorts, and strong employer partnerships, SkillForge is positioned to supply work-ready technicians in HVAC, electrical technology, welding, medical assisting, and automotive service.
Target Customers
There are three major customers of SkillForge. Their actions, demands, and decision stimuli are directly related to the shortages of HVAC, electrical, welding, medical assistant, and automotive work in South Carolina that are recorded.
1. Career-Changing Adults (Primary Segment)
Adults aged 25–50 seeking a faster path into stable technical jobs.
Key needs
- Short programs (6–10 months) that lead directly to employment
- Practice-focused labs instead of long lecture-based classes
- Evening or weekend scheduling
- Industry certifications such as OSHA-10 and EPA 608
- Job placement support and employer access
This segment drives steady year-round enrollment and fills evening and weekend cohorts.
2. Late High School Graduates (Secondary Segment)
Students aged 17–20 who prefer direct-to-work training instead of a four-year degree.
Key needs
- A clear job path within one year
- Training using real equipment
- Affordable tuition and simple enrollment steps
- A supportive campus that feels accessible and career-focused
This group fills daytime cohorts and creates long-term enrollment stability.
3. Employers (Placement Partners) in Need of Trained Technicians
Columbia-area contractors, clinics, auto shops, fabrication firms, and facility maintenance teams.
Key needs
- Entry-level workers are trained on the same tools used in workplaces
- Safety-aware hires who require minimal onboarding
- A reliable, ongoing hiring pipeline
- Direct contact with a placement coordinator
These employers become referral partners and validate the quality of SkillForge graduates.
Competitive Landscape
The vocational training market in Columbia is modest but active, with a mix of state colleges, private trade schools, and smaller career-training providers.
Direct Competitors
| Competitor | Programs Offered | Strengths | Weaknesses |
|---|---|---|---|
| Midlands Technical College | HVAC, welding, and healthcare programs | Well-known institution, lower tuition, established reputation | Long waitlists, limited cohort capacity, slower program updates, and less flexible scheduling |
| Centura College | Trades and medical programs | Private school accessibility, focused career programs | Higher tuition, smaller lab spaces, and limited practicals |
| Fortis College | Medical assisting and select technical programs | Multi-campus brand, recognizable name | Program quality varies, weaker employer connections, and inconsistent placement support |
Indirect Competitors
- Employer-run apprenticeships: Offer paid training but with a limited number of seats and irregularity.
- Four-year colleges: Not direct substitutes, but some of the students who enroll in four-year pathways subsequently transfer to vocational education.
- Online-only trade courses: These are good in theory, but not the lab work needed in HVAC, welding, automotive, or electrical work.
SkillForge’s Competitive Advantages
| Factor | SkillForge’s Advantage |
|---|---|
| Program Length | 6–10-month programs that help students enter the workforce faster |
| Lab Quality | HVAC units, welders, electrical boards, medical simulators, and automotive tools that match industry setups |
| Scheduling | Day, evening, and weekend cohorts for working adults |
| Employer Access | Active partnerships with Columbia-area companies and support from SCDEW referral channels |
| Student Support | Placement help, OSHA-10 and EPA 608 prep, resume coaching |
| Location | Transit-accessible and visible BullStreet District campus close to big employers |
SkillForge differentiates itself as a pragmatic, customizable, employer-linked institution that assists adults in acquiring skilled trades in the shortest time possible with job-ready skills.
Market Trends
The introduction of a new vocational institute in Columbia, South Carolina, can be supported by several trends:
- Chronic shortages of skilled trades: HVAC, electrical, welding, automotive, and medical assisting jobs stay open across the Southeast because employers can’t find enough trained workers. This keeps demand steady for applied training.
- Shift toward short training cycles: Many adults prefer 6–12 month programs over multi-year degrees due to lower cost and faster job entry.
- Local training incentives: South Carolina workforce programs provide dislocated worker training and career changer training that provide stable referral channels via SCDEW.
- Employer preference for job-ready talent: Contractors, healthcare institutions, and auto stores are willing to hire personnel who have real skills to save time onboarding and increase retention.
- Rising interest among high school graduates: The rise of wages in trades and state-based career-consciousness programs has made the short technical programs interesting.
These trends provide a favorable background to such a narrow vocational school as SkillForge, which is an intensive and lab-based school.
Want to create a plan like this for your business?
Create your own plan in minutes using Upmetrics AI

Programs & Delivery Model
SkillForge offers five certificate programs designed for fast entry into technical roles across the Columbia region. All programs follow a 6–10 month schedule and rely on lab-based instruction rather than lecture-heavy formats.
Program List
SkillForge provides the following training programs:
- HVAC Technician
- Electrical Technology
- Welding
- Medical Assisting
- Automotive Service
These programs share a consistent delivery model focused on real equipment, structured lab hours, and job-ready skills that match employer expectations.

Delivery Model
| Component | Description |
|---|---|
| Lab-Based Learning |
|
| Digital Learning Systems |
|
| Cohort Scheduling |
|
Training Capacity (Year 1–3)
SkillForge scales enrollment in line with lab capacity, instructor availability, and market demand.
| Year | Estimated Students | Notes |
|---|---|---|
| Year 1 | 110–125 | Initial intake during the launch and licensing period |
| Year 2 | 160–180 | Growth supported by employer partnerships and stronger referral flow |
| Year 3 | 210–240 | Full lab utilization, multiple cohorts per program, stable placement outcomes |
This growth plan supports manageable program expansion without compromising lab quality or safety.
Training System and Key Suppliers
SkillForge incorporates industry-standard equipment, safety measures, and reliable suppliers to provide technical training across all programs. It aims to ensure the quality of the lab, safe teaching, and equipment that are comparable to what employers operate in the field.
1. Instructional Equipment and Technology
All labs are built to mirror real entry-level work environments:
- HVAC Lab: Trane XR14 training units, refrigerant gauges, recovery systems, and digital diagnostic tools.
- Welding Lab: Miller XMT 350 welders, safety booths, ventilation hoods, and consumables
- Electrical Lab: Fluke multimeter, instructor workboard, work conduit bending, and lockout/tagout
- Medical Assisting Lab: MedLab USA medical mannequins, exam tables, ECG machines, and simple clinical supplies.
- Automotive Lab: Vehicle lifts, Snap-on diagnostic equipment, service equipment.
This setup lets students work with the same tools and equipment they will use on the job.
2. Learning Platforms and Software
SkillForge uses established education and operations tools:
- Canvas LMS coursework, testing, and communication.
- JobConnect Career Portal is a job placement tracking and employer match program.
- QuickBooks Enterprise accounting, Payroll, and Financial reporting
These platforms help maintain consistent instruction, tracking, and program oversight.
3. Safety and Compliance
Lab operations follow state and federal safety standards:
- OSHA standards are used to direct welding, electrical, and HVAC laboratory activities.
- Fire marshal inspections confirm ventilation, equipment spacing, and emergency systems.
- Teachers conduct frequent maintenance of equipment and safety briefings.
This ensures safe student training and reduces operational risk.
4. Supplier Partnerships
SkillForge partners with trusted education and industry suppliers:
- Miller Electric for welders
- Snap-on for automotive tools
- Fluke for electrical testing gear
- Trane for HVAC units
- MedLab USA for medical assisting equipment
Vendors provide service agreements to maintain equipment performance and reduce downtime.
Programs and Student Services
SkillForge offers hands-on certification programs and support services designed to help students enter HVAC, electrical, welding, medical assisting, and automotive roles quickly and confidently.
Additional Training Offerings & Student Experiences
OSHA-10 Certification
Price: $125
Description: Safety credentials are required for construction and industrial workplaces.
Note: Included for selected programs.
EPA 608 Certification Exam Prep
Price: $95
Description: Required credential for HVAC technicians working with refrigerants.
Note: Offered as an add-on or bundled with the HVAC program.
Career Services Workshops
Price: Included
Description: Resume building, mock interviews, job search help, and employer meet-and-greets.
Note: Supports placement for all programs.
Open Lab Saturdays
Price: Included for enrolled students
Description: Extra practice hours supervised by instructors for welding, electrical, HVAC, and automotive labs.
Note: Helps students strengthen practical skills.
Campus Systems & Efficiency Measures
SkillForge focuses on running a safe, well-equipped training campus with systems that keep teaching consistent and operating costs under control.
The school uses structured lab procedures, equipment maintenance plans, and safety protocols so instructors can teach effectively and the campus can run smoothly every day.
- Energy consumption: LED lighting energy consumption, welding and HVAC lab ventilation controls, and programmed equipment shutdowns are used to lower the power bills.
- Tool and equipment lifecycle planning: Miller, Snap-on, Trane, and Fluke service agreements minimize downtime with no cause and increase equipment lifecycle.
- Water and facility management: Closed-loop cooling and waste-capture systems facilitate welding and HVAC training
- Consumables management: Welding rods and medical supplies are consumable materials, which are ordered in large quantities to eliminate cost variations.
- Regulatory readiness: Complete OSHA and fire safety in all labs to decrease the risk of operations.
The systems assist SkillForge in ensuring quality and consistency of the lab and also regulating the current campus operational expenses.
Operations & Staffing
SkillForge has day and evening cohorts that suit the working schedules and schedules of employers.
Operating Hours
- Monday–Friday: 8:00 AM to 8:30 PM
- Saturday: 9:00 AM to 3:00 PM (labs only)
Shift Structure
- Day Shift: 8:00 AM to 2:00 PM
- Evening Shift: 3:00 PM to 8:30 PM
Daily Workflow
The day of SkillForge starts with the opening of labs by the instructors, safety checks, and setting up stations at 8:00 AM before the morning cohort. Classes operate during the mid-day, and admissions oversees the inquiries, student tours, and enrolments. By mid-afternoon, the labs are washed and prepared to do the evening group.
The evening session commences at 3:00 PM until 8:30 PM, consisting of hands-on lab work, credential preparation, and open practice time. During closing, instructors update equipment records, lock the room, and finish administration tasks to get the campus ready to start the next day.
Staffing Plan
| Role | Staff Needed | Job | Pay |
|---|---|---|---|
| Campus Director | 1 | Oversees campus operations, compliance, and staffing | $110,000/year |
| HVAC Instructor | 1 | Lab instruction, safety checks, credential prep | $66,000/year |
| Electrical Instructor | 1 | Electrical labs, safety supervision, assessments | $68,000/year |
| Welding Instructor | 1 | Welding booths, metal prep, skill testing | $62,000/year |
| Medical Assisting Instructor | 1 | Clinical labs, simulations, student testing | $58,000/year |
| Automotive Instructor | 1 | Diagnostics, shop safety, hands-on practice | $65,000/year |
| Admissions Staff | 2 | Student intake, tours, enrollment | $45,000/year each |
| Career Services Coordinator | 1 | Placement, employer liaison, job fairs | $52,000/year |
| Administrative Assistants | 2 | Scheduling, records, and front-desk operations | $37,000/year each |
| Facilities & Maintenance | 1 | Lab upkeep, equipment checks, repairs | $39,000/year |
SkillForge cross-trains staff for scheduling flexibility and uses vendor service contracts to reduce internal maintenance workload.
Vendor & Partner Network
SkillForge also has service relationships that ensure the operation of its laboratories, which are safe and functional and adhere to standards in the workplace. Such relationships provide uptime of equipment, periodic calibration, and compliance in the HVAC, welding, electrical, medical assisting programs and automotive programs.
| Vendor | Role | Agreement Scope |
|---|---|---|
| Trane Education Solutions | HVAC training units | Annual inspection and performance checks |
| Miller Electric | Welding machines and booths | Warranty coverage and yearly maintenance |
| Snap-on Industrial | Automotive diagnostic tools | Multi-year tool supply and calibration plan |
| Fluke | Electrical testing instruments | Annual calibration and safety checks |
| MedLab USA | Medical simulation and clinical supplies | Replacement and service package |
| CPA Firm | Accounting and compliance | Quarterly reviews and lender reporting |
The agreements ensure that the equipment of SkillForge is in good calibration, they minimise downtime, and contribute to the correct regulatory reporting. All contracts are reviewed by the campus director on an annual basis in order to contain costs and ensure the quality of the programs.
Technology Integration
SkillForge is a company that provides digital tools for direct instruction, safety, operations, and compliance.
- Canvas LMS: Assignments and grading, surveys and assessments, and instructor email
- JobConnect Portal: Job postings, employment matching, and placements.
- QuickBooks Enterprise: Accounting, payroll, and lender reporting
- Lab Safety Systems: Welding ventilation sensors, electrical lockout–tagout controls, HVAC diagnostic readouts
- Digital Equipment Logs: Tracks service intervals for welders, HVAC units, electrical trainers, and medical simulators
- Attendance & Progress Dashboards: Track student hours, completion rates, and credentials
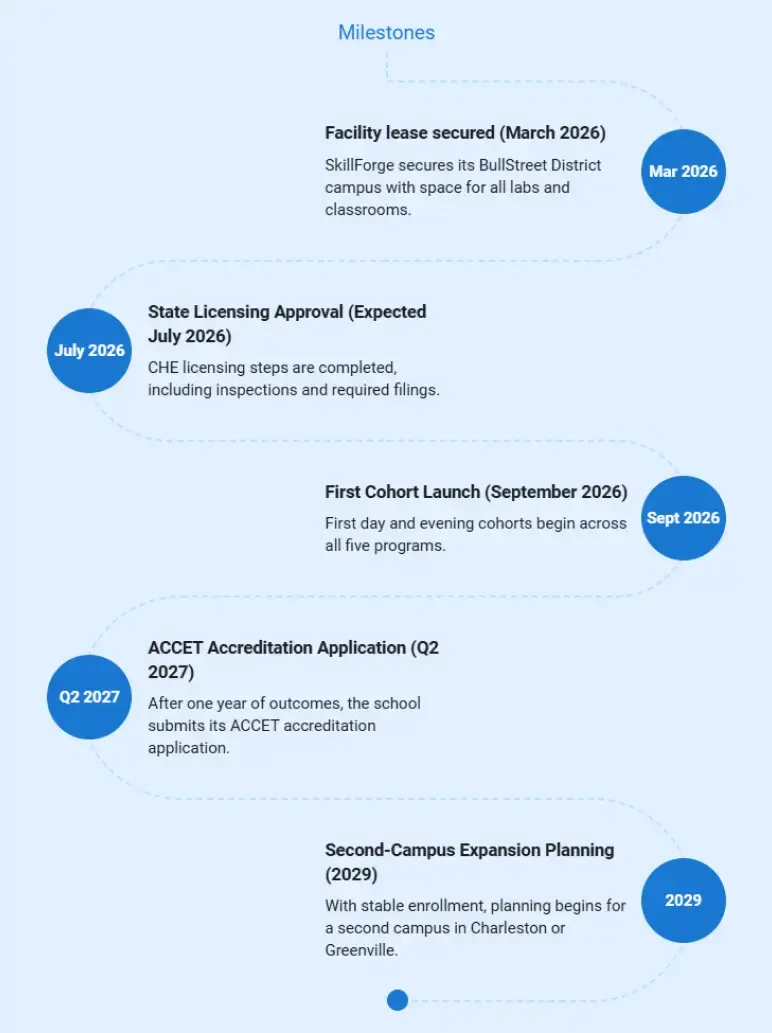
Milestones & Timeline
SkillForge Technical Vocational Institute has a clear growth plan with key milestones and dates that guide the school from initial buildout to full enrollment and stable, profitable operations.
Compliance & Regulatory Management
SkillForge will adhere to all state and federal requirements for technical training centers:
- South Carolina Commission on Higher Education licensing: Required for postsecondary schools offering certificate programs.
- OSHA lab safety requirements: Welding, HVAC, and electrical labs are bound to adhere to the federal rules of workplace safety.
- Fire marshal inspections: This is required for welding ventilation, exits, fuel storage, and emergency systems.
- ACCET Accreditation (target Year 2): Strengthens program credibility and supports future funding eligibility.
- Americans with Disabilities Act (ADA) facility standards: Provide access to all students to buildings.
- Data privacy compliance: Records of students under FERPA guidelines.
Sales & Marketing Strategy
Strategic Objective
SkillForge seeks to sustain consistent enrollment using three main sources, which are workforce-agency referrals, search-based online queries, and collaborations with high schools and employers. The initial target is high-intent online traffic and workforce referrals; in Year 2, the funnel is widened by robust employer and school partnerships.
Enrollment Channels
SkillForge employs three regular avenues of attracting students:
- Workforce Referrals (approximately 30-40%)
Adults who are employed and receive financial assistance in workforce programs, and are willing to undertake brief, employment-oriented training.note
- Direct Digital Enrollment (approximately 40-50%)
Search ads generate high-intent prospects for HVAC, welding, electrical, medical assisting, and automotive programs.
- School, Community, and Employer Partnerships (about 20%)
There is consistent auxiliary volume provided by high school counselors, community workshops, and employer relationships.
Marketing Budget & Activities
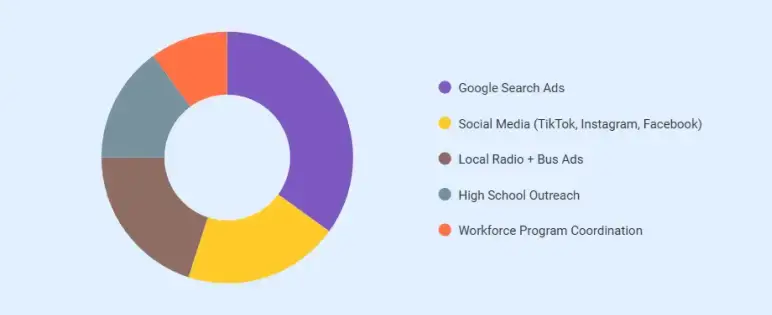
SkillForge allocates $3,000 per month in Year 1, increasing to $4,200 per month by Year 3, split across key channels:
| Activity | Share | Purpose |
|---|---|---|
| Google Search Ads | 35% | Capture high-intent training searches |
| Social Media | 20% | Show lab demos and student outcomes |
| Radio + Bus Ads | 20% | Build local awareness in commuting corridors |
| High School Outreach | 15% | Reach non-college-bound seniors |
| Workforce Coordination | 10% | Maintain agency referral flow |
Promotions & Community Activities
SkillForge uses simple promotional efforts that align with its vocational focus:
- “Try the Trade” Lab Days: Monthly open-lab events where prospective students can see welding, electrical, HVAC, and medical assisting stations.
- Career Restart Scholarships: Minor tuition breaks for unemployed workers who are referred through workforce agencies.
- High School Technical Workshops: Short talks in the schools to demonstrate to the seniors the possibilities available in technical professions.
- Meet-and-Greets with the employer: The meetings with the students are three or four times a year, and this increases the rates of placement.
- Social Media Demonstrations: Videos depicting work in the laboratory, tips by the teacher, and student stories of success.
Enrollment Targets and Student Acquisition Plan
| Year | Key Focus | Customer Acquisition Goals | Total Revenue ($) | Workforce Referral Share | Direct Enrollment Revenue ($) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Year 1 | Establish the Base | Build awareness, secure SCDEW referral channel, launch digital campaigns | $1.20M–$1.35M | 30% | ~$900,000 |
| Year 2 | Expand pipeline | Add high school partnerships and veteran intake; strengthen employer links | $1.75M–$2.05M | 35% | ~$1.30M |
| Year 3 | Scale Enrollment | Multiple cohorts per program; deeper employer integration | $2.30M–$2.70M | 40% | ~$1.60M |
Notes:
- Workforce referral share reflects the % of enrolled students coming from SCDEW and related programs.
- Direct enrollment revenue covers the students who are also gained via search advertisement, social media, and community outreach
- Year 2 to Year 3 growth will be fuelled by increased collaborations, improved placement performance, and increased brand awareness in Columbia
The combination of workforce referrals, direct enrollment, and employer integration results in a stable, predictable pipeline of enrollment by Year 3.
Financial Plan
SkillForge’s financial plan is based on realistic enrollment growth, verified payroll costs, and the operating profile of a technical training campus.
Startup Costs
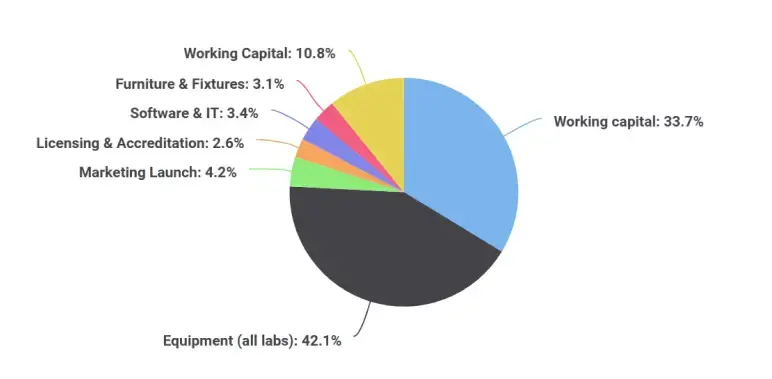
SkillForge would have to invest in the campus, furnish the laboratories, undergo the licensing process, and prepare the first cohort, and this would cost it $831,000.
| Category | Description | Amount (USD) |
|---|---|---|
| Facility Buildout | HVAC, welding, electrical, medical, and automotive lab installation | $280,000 |
| Equipment (all labs) | Trane HVAC units, Miller welders, Snap-on tools, electrical boards, and medical simulators | $350,000 |
| Marketing Launch | Search ads, outreach, media | $35,000 |
| Licensing & Accreditation | SC Commission licensing, prep for ACCET | $22,000 |
| Software & IT | Canvas LMS, JobConnect, QuickBooks, IT setup | $28,000 |
| Furniture & Fixtures | Classrooms, offices, storage | $26,000 |
| Working Capital | 4–5 months of operating buffer | $90,000 |
| Total Required Capital | ≈ $831,000 |
SkillForge has a total capital of $1.25 million to raise:
- State Workforce Development Grant: $420,000.
- TD Bank Education Loan: $650,000
- Owner Equity: $180,000
Total Available Capital: $1,250,000
This is more than the cost of startup by about $419,000, which is the operating buffer that is required by the school.
Important Assumptions
- Increase of 110-125 students in Year 1 to 210-240 in Year 3.
- Tuition fees are between 9,900 and 14,200 on average, depending on the program.
- Payroll remains roughly 55 % of operating costs
- Marketing increases gradually as programs scale
- Working capital covers 3–4 months of operating expenses
- Loan term: 10 years at 8.6 % fixed interest
- Placement rates and stronger employer ties improve retention
- No revenue from federal student aid is assumed until after accreditation
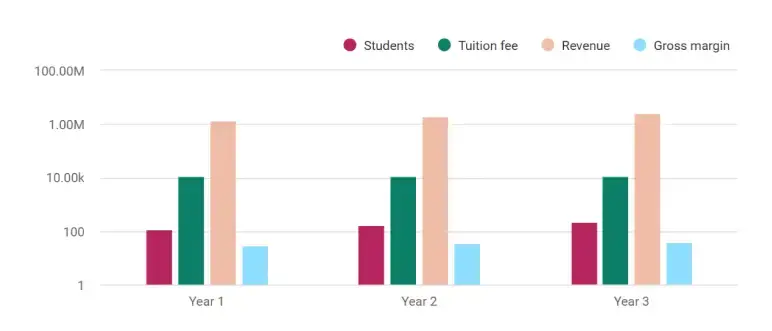
Revenue Forecasts
| Year | Students | Avg Tuition | Revenue | Gross Margin |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 120 | ~$11,000 | $1,320,000 | ~30% |
| 2 | 170 | ~$11,200 | $1,904,000 | ~35% |
| 3 | 225 | ~$11,400 | $2,565,000 | ~38% |
Operating Costs (Annual Breakdown)
| Expense category | % of Total | Annual Cost Range |
|---|---|---|
| Instructor Payroll | ~45% | $420,000–$460,000 |
| Utilities & Lab Safety Systems | ~10% | $110,000–$130,000 |
| Equipment Service & Consumables | ~12% | $140,000–$160,000 |
| Marketing & Enrollment | ~8% | $95,000–$115,000 |
| Administrative Salaries | ~15% | $170,000–$190,000 |
| Insurance, Licensing, Compliance | ~10% | $110,000–$125,000 |
Total Operating Costs: Approximately $1.05–$1.28 million per year at steady-state enrollment.
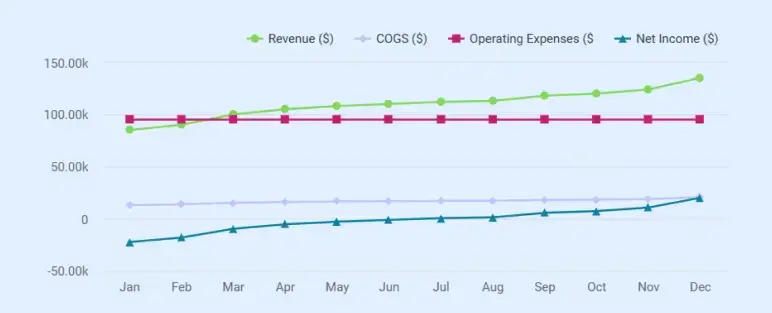
Monthly Projections (Year 1)
| Month | Revenue ($) | COGS ($) | Operating Expenses ($) | Net Income ($) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Jan | 85,000 | 12,800 | 95,000 | -22,800 |
| Feb | 90,000 | 13,500 | 95,000 | -18,500 |
| Mar | 100,000 | 15,000 | 95,000 | -10,000 |
| Apr | 105,000 | 15,700 | 95,000 | -5,700 |
| May | 108,000 | 16,200 | 95,000 | -3,200 |
| Jun | 110,000 | 16,500 | 95,000 | -1,500 |
| Jul | 112,000 | 16,800 | 95,000 | +200 |
| Aug | 113,000 | 17,000 | 95,000 | +1,000 |
| Sep | 118,000 | 17,700 | 95,000 | +5,300 |
| Oct | 120,000 | 18,000 | 95,000 | +7,000 |
| Nov | 124,000 | 18,600 | 95,000 | +10,400 |
| Dec | 135,100 | 20,300 | 95,000 | +19,835 |
| Total | $1,320,000 | ~$198,000 | $1,140,000 | -$234,000 |
Projected Profit & Loss Statement (3 Years)
| Category | Year 1 | Year 2 | Year 3 |
|---|---|---|---|
| Total Revenue | $1,320,000 | $1,904,000 | $2,565,000 |
| COGS (lab consumables, repairs, service contracts) | $198,000 | $285,600 | $384,750 |
| Gross Profit | $1,122,000 | $1,618,400 | $2,180,250 |
| Operating Expenses (payroll + utilities + insurance + marketing) | $1,140,000 | $1,220,000 | $1,285,000 |
| EBITDA | –$18,000 | $398,400 | $895,250 |
| Depreciation (equipment + improvements) | $60,000 | $60,000 | $60,000 |
| EBIT | –$78,000 | $338,400 | $835,250 |
| Loan Payments (principal + interest) | $100,000 | $100,000 | $100,000 |
| Net Income (Before Tax) | –$178,000 | $238,400 | $735,250 |
Projected Balance Sheet (3 Years)
| Category | Year 1 | Year 2 | Year 3 |
|---|---|---|---|
| ASSETS | |||
| Current Assets | |||
| Cash & Working Capital | $90,900 | $250,000 | $640,250 |
| Accounts Receivable | $110,000 | $155,000 | $205,000 |
| Prepaid Expenses & Deposits | $25,000 | $20,000 | $20,000 |
| Inventory (lab supplies + consumables) | $18,000 | $22,000 | $26,000 |
| Total Current Assets | $243,900 | $447,000 | $891,000 |
| Fixed Assets | |||
| Facility Buildout (net) | $280,000 | $240,000 | $200,000 |
| Equipment (all labs, net) | $350,000 | $310,000 | $270,000 |
| Furniture & Fixtures (net) | $26,000 | $20,000 | $15,000 |
| Software & IT (net) | $28,000 | $20,000 | $12,000 |
| Total Fixed Assets | $684,000 | $590,000 | $497,000 |
| TOTAL ASSETS | $927,900 | $1,037,000 | $1,388,250 |
| LIABILITIES & EQUITY | |||
| Current Liabilities | |||
| Accounts Payable | $70,000 | $85,000 | $95,000 |
| Accrued Payroll & Benefits | $55,000 | $60,000 | $65,000 |
| Current Portion of Loan | $65,000 | $65,000 | $65,000 |
| Total Current Liabilities | $190,000 | $210,000 | $225,000 |
| Long-Term Liabilities | |||
| Long-Term Portion of Loan | $585,000 | $520,000 | $455,000 |
| Total Liabilities (Current + Long-Term) | $775,000 | $730,000 | $680,000 |
| Owner’s Equity | |||
| Owner Capital (initial equity) | $180,000 | $180,000 | $180,000 |
| Retained Earnings | –$27,100 | $127,000 | $528,250 |
| Total Owner’s Equity | $152,900 | $299,000 | $700,000 |
| TOTAL LIABILITIES & EQUITY | $927,900 | $1,037,000 | $1,388,250 |
Spreadsheets are exhausting & time-consuming
Build accurate financial projections w/ AI-assisted features

Projected Cash Flow (3 Years)
| Category | Year 1 | Year 2 | Year 3 |
|---|---|---|---|
| CASH INFLOWS | |||
| Owner Equity Contribution | $180,000 | — | — |
| Grant Funding | $420,000 | — | — |
| Bank Loan Received | $650,000 | — | — |
| Revenue Collected | $1,320,000 | $1,904,000 | $2,565,000 |
| Total Cash Inflows | $2,570,000 | $1,904,000 | $2,565,000 |
| CASH OUTFLOWS | |||
| Facility Buildout | $280,000 | — | — |
| Lab Equipment (HVAC, welding, automotive, medical) | $350,000 | — | — |
| Software & IT Setup | $28,000 | — | — |
| Furniture & Fixtures | $26,000 | — | — |
| Licensing & Accreditation | $22,000 | — | — |
| Working Capital Reserve | $90,000 | — | — |
| Marketing Launch | $35,000 | — | — |
| Operating Expenses | $1,140,000 | $1,220,000 | $1,285,000 |
| COGS | $198,000 | $285,000 | $384,750 |
| Loan Payments (Principal + Interest) | $100,000 | $100,000 | $100,000 |
| Maintenance & Utilities | $40,000 | $45,000 | $50,000 |
| Capital Replacement (small equipment refresh) | — | $20,000 | $40,000 |
| Total Cash Outflows | $2,309,000 | $1,670,600 | $1,859,750 |
| NET CASH FLOW (before tax) | $261,000 | $233,400 | $705,250 |
| Beginning Cash Balance | — | $261,000 | $494,400 |
| Ending Cash Balance | $261,000 | $494,400 | $1,199,650 |
Break-Even Analysis
| Metric | Amount |
|---|---|
| Average Tuition per Student | $11,200 |
| Variable Cost per Student | $1,725 (≈15% COGS based on program consumables and lab materials) |
| Contribution Margin per Student | $9,775 |
| Annual Fixed Costs | ≈$1.28M (payroll, rent, insurance, software, loan payments, admin) |
| Break-Even Volume (students per year) | 1,280,000 ÷ 9,775 ≈ 130.9 ≈ 131 students |
| Break-Even Revenue | 131 × $11,200 = $1,467,200 |
| Current Year 1 Enrollment | 120 students |
| Coverage | ≈92% of break-even |
Business Ratios
| Ratio | Formula / Definition | Year 1 | Year 2 | Year 3 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Gross Margin | Gross Profit ÷ Revenue | 85% | 85% | 85% |
| Net Profit Margin | Net Income ÷ Revenue | -13% | 12% | 28% |
| Current Ratio | Current Assets ÷ Current Liabilities | 2.16 | 3.28 | 5.86 |
| Debt-to-Equity Ratio | Total Liabilities ÷ Owner’s Equity | 2.43 | 1.25 | 0.56 |
| Return on Assets (ROA) | Net Income ÷ Total Assets | -16% | 18% | 39% |
| Return on Equity (ROE) | Net Income ÷ Owner’s Equity | -56% | 41% | 61% |
| Operating Expense Ratio | Operating Expenses ÷ Revenue | 86% | 64% | 50% |
| Break-Even Coverage Ratio | Actual Sales ÷ Break-Even Sales | 0.92 | 1.26 | 1.67 |
Funding Requirements
Loan Overview
SkillForge requires funding for facility buildout, lab equipment, software systems, staffing, licensing, and early operating reserves. Total startup capital required is approximately $1.25 million.
Funding Sources
- State Workforce Development Grant: $420,000
- TD Bank Education Loan: $650,000 (10 years, 8.6 % fixed)
- Owner Equity: $180,000
Total Available Capital: $1,250,000
This exceeds the $831,000 initial cost estimate and provides a reserve buffer for 4–5 months of early operations.
Purpose of the Loan
Loan proceeds will be used for:
- Construction and setup of HVAC, welding, electrical, medical assisting, and automotive labs
- Buy Trane HVAC, Miller welders, Snap-on tools, electrical boards, and medical simulators
- Furniture, teaching stations, and IT/LMS installation on campus
- Accreditation, preparation of licensing and regulatory filings
- First monthly salaries, advertisement, and a four to five-month working capital margin
This structure allows SkillForge to complete the buildout and support its first cohorts while reaching stable operations.
Collateral Summary
The loan will be backed by:
- Lab equipment and tools: $350,000
- Leasehold improvements: $280,000
- IT systems, furniture, fixtures: $54,000
- Personal guarantees from all owners
This provides adequate collateral coverage for the loan request.
Repayment Plan & DSCR
Based on the financial model:
- Year 1 DSCR: below 1.0 (startup phase)
- Year 2 DSCR: strong coverage supported by higher enrollment
- Year 3 DSCR: stable repayment capacity
The owners’ equity contribution reduces lender risk and supports healthy cash reserves.
The Quickest Way to turn a Business Idea into a Business Plan
Fill-in-the-blanks and automatic financials make it easy.



