An exciting business idea strikes us all once in a while. While most of them end up in the rubble, some ideas persuade us enough to chase them.
Now, the journey between an idea and its business actualization is a long road. The first step towards this journey begins with idea validation.
How do you do that?
With a business model canvas!
A business model canvas compels you to think about all the aspects of your business without overwhelming you with the detailed nuances of business planning. It’s a strategic tool that will help you gain clarity and vision.
But how to use the business model canvas?
Let’s learn that in this blog post through an example and some practical tips.
Let’s get started.
What is a business model canvas?
Business Model Canvas (BMC) is a single-page strategic management tool developed by Alexander Osterwalder. It helps you summarize and validate your business using nine simple boxes, each representing an important business component.
The layout of the BMC is predetermined with the value proposition taking a center place. The remaining eight blocks of BMC include customer segments, channels, customer relationships, key resources, key partnerships, key activities, cost structure, and revenue model.
Also known as the 9 building blocks, these components in the canvas help you to get an overview of your entire business on a single canvas.
When presented visually, this is how a business model canvas looks:

As you can see, all the essential business components lay on the same page, making your entire idea easy to digest.
How to use a business model canvas?
Since the layout of BMC is quite fixed, let’s simply dive into understanding what each of the 9 boxes entails.
The right side of the BMC represents market aspects (external factors) while the left side entails business aspects (internal factors). At the center lies a value proposition that ties together all the aspects through a common core value.
With that said, let’s understand the proper way to use a business model canvas with a real-life example.
1. Customer segments
Start this section by answering the most basic question—who would choose my product or service?
This will help identify the customer base for your business.
In the case of Airbnb, this rental platform serves two diverse customer groups—travelers and property hosts. While the former gets accommodation options from Airbnb, the latter earns income by listing their properties on Airbnb.
Now, identify the individuals with similar attributes (i.e. age, gender, income, needs) from your customer base and group them.
Try answering these questions to determine your customer segment:
- What are the characteristics of people that will benefit from my product or service?
- Do they belong to a specific geographic area?
- Do they belong to a specific income group?
- What aspect of my value proposition appeals to them?
You can also use customer persona templates to build customer profiles of different customer segments here.
In the case of AirAirbnb, we have to create segments for travelers as well as property hosts.
As for the travelers, Airbnb can satisfy the needs of
- Experience seekers
- Leisure travelers
- Business travelers
- Short and long-term renters
Considering the income levels, Airbnb would have listings for both budget and luxury spenders.
As for the property hosts, Airbnb targets
- Homeowners
- Property managers
- Real estate investors
Once you have the customer segments ready, you move to the next step determining the value you have to offer.
2. Value proposition
The value proposition is at the center of any business model canvas for a reason. It ties together your entire business idea addressing the most important question: What is it that the customers get from your business?
Mind you, the value proposition isn’t about the product or idea. It’s about the pain or problem you’re trying to solve.
Let me give you 3 simple questions, that will help you define your value proposition:
- What is the problem I am solving?
- What is the need I am addressing?
- How is my product/service getting the customer’s job done?
Now, let’s understand this with our Airbnb example.
Airbnb caters to two broad customer segments—travelers and hosts.
As for the travelers, why would they choose to stay in Airbnb properties and not the traditional hotels?
- Unique and diverse accommodations
- Personalized and immersive local experience
- Budgeted stays
- Trust and safety
- Host ratings
Airbnb establishes trust through host ratings and doesn’t compromise on the quality of stay and safety—the two primary concerns for any traveler. This makes it easier for travelers to choose Airbnb over hotels.
As for the hosts, what value do they gain by listing on Airbnb?
- Income generation
- A large marketplace of travelers
- Host support services
- Property protection plan
Airbnb addresses the host’s concerns about property damage with stringent protection plans and customer support. It has started offering guest ratings as well to help hosts make better decisions.
3. Customer channels
After identifying the customer segments and value proposition, determine how you will communicate and deliver the products to your customers.
This includes the channels through which the potential customer will come in contact with your business. This can be through a physical outlet, a digital medium, or both.
For instance, Airbnb communicates and delivers its services to its customers (hosts and travelers) through websites and apps.
As for the marketing and sales channels, customers find them mostly through social media and word-of-mouth appreciation.
However, they have a few other strategies and techniques to reach the customers. This includes:
- Travel events
- Discounts and referral codes
- Media coverage
- Paid ads
All these together constitute the channels for their BMC model.
4. Customer relationships
With established channels to reach target customers, let’s see how we will interact with customers through them. In this section of BMC, identify the type of relationship your customer expects you to maintain.
Well, we have a few questions that will help determine the customer relationships for your business:
- How do we engage with customers before, during, and after a purchase?
- Do customers prefer personal, automated, or self-service interactions?
- How do customers prefer to get support (phone, email, chat)?
- How do we measure and improve customer satisfaction and loyalty?
Creating a customer journey map at this point can be helpful. It will help clarify the points of engagement between you and your business and present the opportunities for automation.
Continuing our Airbnb example, let’s understand how it maintains customer relationships for travelers and hosts.
Here are the Airbnb’s relationships with travelers:
- Self-service approach to make bookings.
- Dedicated assistance to resolve queries.
- Guests incentives and referral bonuses for customer loyalty.
- Self-automated process for verification.
- Guest reviews and communities to establish trust.
Here are the Airbnb’s relationships with hosts:
- Self-service app to manage bookings and listings.
- Email and call support to resolve queries.
- Superhost programs to enhance visibility.
- Host reviews to establish trust.
5. Revenue streams
Revenue streams outline your methods to convert key value propositions into income.
Here you consider all the primary and secondary sources that will bring you money. So think thoroughly and assess different revenue situations to fill this section.
Here are a few revenue streams popularly used by different business models:
- In-store sales
- E-commerce or website sales
- Subscription services
- One-time fees
- Transaction based fees
- Freemium services
- Add-ons pricing
- Licensing fees
- Advertisements
For our Airbnb example, this business earns revenue by charging transaction-based commissions from guests and hosts.
With that, we have addressed all the internal aspects of our business model. Let’s now move to the left side of the BMC model.
6. Key activities
Key activities refer to the specific activities and tasks that help you:
- Deliver your value propositions
- Reach your customer segments
- Maintain relationships
- Generate revenue
It doesn’t matter if you’re performing certain tasks in-house or getting it outsourced. As long as the activity is crucial for your business operations it is included in the key activities.
Let’s get a more practical overview by understanding the key activities for Airbnb.
- Development and maintenance (app + website)
- Customer support services
- Host onboarding and training
- Curating new offerings
- Digital marketing activities
- Making strategic partnerships (insurance provider)
- Hiring strategic assets and collaborators
7. Key resources
In this section of canvas, you highlight the key resources essential to performing your key activities.
These resources include:
- Physical: inventory, equipment, tools, office space
- Technological: website, app, servers, analytic systems
- Human: employees, contractors, freelancers
- Intellectual: patent, trademark, copyright, etc.
- Capital: money, loans, etc.
For our Airbnb example, here are the key resources this property rental platform requires.
- Website
- App
- Airbnb office space (globally)
- Staff
- Data assets
8. Key partnerships
Key partnerships refer to the external companies, suppliers, contractors, and individuals who would help perform the key activities you can’t perform yourself.
Every business needs a key partner, even individually owned-businesses.
For instance, someone selling cakes from home would have partnerships with stores to get cake supplies, delivery partners to deliver the cakes, and a payment gateway to accept online payments.
Continuing the example of Airbnb, the key partners for this company are:
- Property renters and hosts
- Insurance providers
- Travel and tourism boards
- Professional photographers
- Community managers
- Third-party travel platforms
9. Cost structure
The last part of the business model canvas helps outline the cost structure of your business.
Here you talk about the costs of performing business’s key activities, acquiring key resources, and paying your key partners. Basically, the overall cost of creating and delivering your value proposition.
Since you have already identified your main resources, partnerships, and activities, this step is going to be easier. However, before you evaluate your cost streams, determine if yours is a value-driven or cost-driven business.
Let’s put together the last piece of our Airbnb business canvas model. Its cost structure would include expenses for:
- Technology development
- Marketing
- Customer support
- Employee salaries
- Transaction costs(payment processors)
- Insurance costs
Here’s a completed business model canvas example for Airbnb
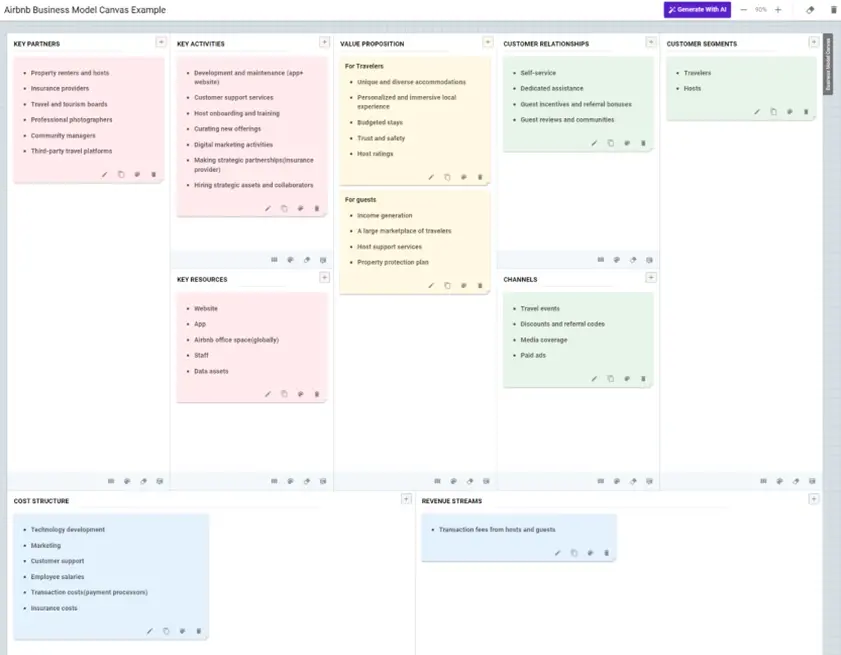
With that, you have filled all the blocks of the canvas. Now, we have a few more examples for you to get a better understanding of the BMC model.
Business model canvas examples
Check these examples of real-life companies and their business model canvas.
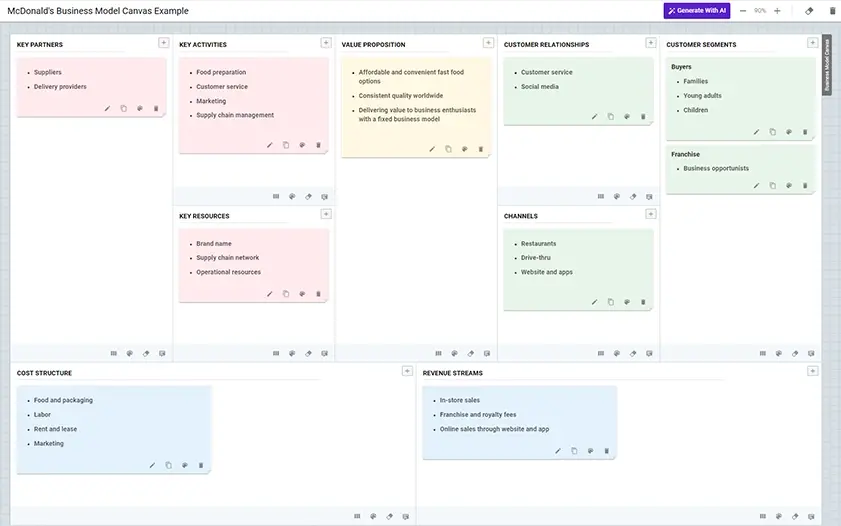
Mcdonald’s business model canvas
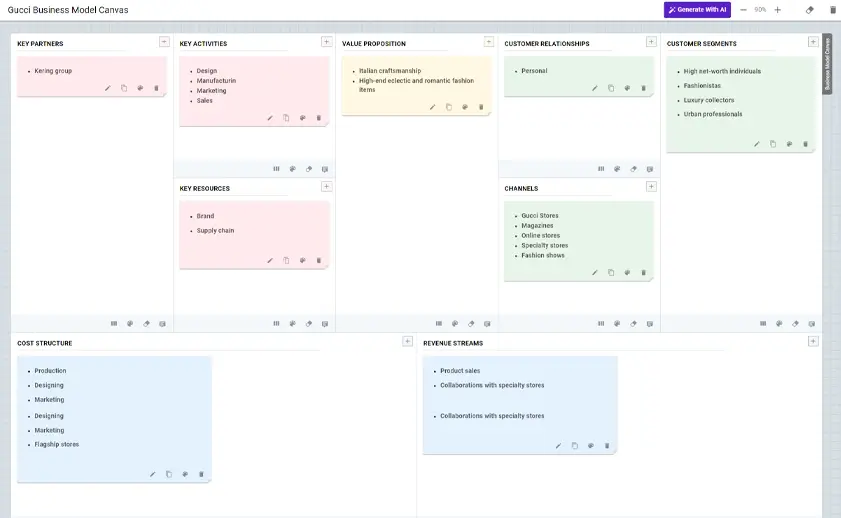
Gucci business model canvas
Tips to write a business model canvas
We have gathered these quick tips for you to help you approach the BMC appropriately. Check them out.
1. Make the right start
We interviewed a couple of entrepreneurs for their insights on BMC, and most of them recommended starting with customer segments or value propositions.
This insight by Chris Yang, the co-founder at Coins Value shows the benefit of starting your canvas with a customer segment.
“My recommendation for entrepreneurs is to start with the Customer Segments building block. By deeply understanding your target audience’s needs, desires, and behaviors, you’ll unlock the key to crafting a truly resonating value proposition. From there, systematically work through the remaining blocks, allowing each element to inform and refine the others.”
2. Revisit and reiterate
Almost everyone that we interviewed for this article, suggested revisiting the business model canvas time and again.
Remember, there’s no price in finishing it early or quickly.
While addressing different segments of BMC, you may find a conflicting approach or strategy to your original ideas. Be brutally honest and remain open to adjusting your ideas during this exercise.
Consider BMC as a business model innovation tool to spark discussion and ideas. Don’t get too hung up on perfecting it. Instead, use it as a tool to help you think thoroughly.
3. Be very specific and brief
Don’t undertake this exercise for the sake of having a model canvas. Avoid vagueness by asking the right questions. Refer to similar business models and try finding specific answers for each section.
You don’t need to offer more detail here. For instance, no need to discuss your marketing strategies and pricing plan here. You have a business plan to explore depths.
For now, focus on pulling together all the aspects with brevity.
4. Make it collaborative
If you have people in marketing, sales, operations, and finances, get them onboard and fill in this canvas together. A healthy discussion can spark ideas and make this process extremely fruitful.
Conclusion
The 9 building blocks of the business model canvas offer a holistic overview of your business ensuring alignment across all the business components. From the largest multinational to the bootstrapped startups—every business regardless of its size can be described with these 9 building blocks on a single sheet of paper.
Now, you can easily find a business model canvas template online. However, if you’re looking for a strategic tool that allows you to collaborate and streamline your planning approach, Upmetrics can help.



