Imagine presenting your business idea to a room full of Shark investors.
While your passion and creativity might spark their interest, it’s the numbers in your business plan, particularly your financial projections, that will make or break the deal.
These projections will help answer questions such as:
- When will your business break even?
- How much sales will you generate in the first year?
- What’s your annual recurring revenue (ARR) potential?
- What’s your gross profit margin or burn rate?
By combining your vision with well-researched financial projections, your business plan becomes a blueprint for growth and profitability.
With this blog post, let’s understand the components of financial projections and get a step-by-step guide to building one.
What are financial projections in a business plan?
Financial projections are a key element of the financial plan, which serves as a critical component of your overall business plan.
They provide estimates of your company’s future financial performance, based on realistic assumptions about your current position, market trends, and, past performance (if applicable).
Financial projections validate the business’s expected growth and sustainability. It helps assure investors that you have a clear plan to generate returns and manage finances effectively.
As a startup, projections help prepare for the first few years guiding you to make key strategic decisions.
Financial plan vs. financial projections
Short answer: A startup financial plan is an integral part of a traditional business plan, whereas financial projections are part of a financial plan.
To define both:
A financial plan is a critical section of a business plan. It outlines your business’s current financial position, future goals, and strategies for achieving these goals as well as the financial projections.
Financial projections are forecasts of a company’s future financial performance, based on current data, realistic assumptions, and market trends.
Investors pay close attention to these projections to understand the business’s sustainability, scalability, and profitability over the next few years.
Business plan > Financial Plan > Financial projections
There’s no confusion—your business plan is the overarching document, a financial plan is a section of a business plan, and financial projections are part of the financial plan.
Say goodbye to old-school Excel and spreadsheets
Make realistic financial projections in minutes!

Key components of business plan financial projections
Now the most important question: What should your business plan financial projections include?
Your financial projections should include three essential financial statements: cash flow statement, balance sheet, and income statement along with break-even analysis.
Depending on the purpose of your startup financial plan, you may create yearly projections or multi-year financial projections for 3 to 5 years.
Let’s view them:
1. Cash flow statement
The cash flow statement projects the movement of money moving in and out of a business, reflecting its ability to generate and manage liquidity. While it helps visualize the business’s cash situation, it also guides you to make important decisions to ensure healthy cash flow.
Investors typically require at least two years of cash flow projections to assess your ability to repay loans or manage operational costs.
Here are the fundamental blocks that will build your cash projections:
| Activities | What it includes |
|---|---|
| Operating activities |
|
| Financing activities |
|
| Investing activities |
|
2. Income statement
An income statement, also known as a profit and loss statement, forecasts the business’s revenue and expenses over a specific period in the future. It evaluates overall profitability and provides insights into its operational efficiency and financial health.
Income statements are created using these components:
- Revenue: Income from selling your products/services
- Cost of Goods sold: Direct costs involved in producing products or delivering services
- Operating expenses: Expected costs to keep your business running
- Interests, tax, depreciation, and amortization: Additional income/expenses such as interest income, dividends, tax payouts, and depreciation
3. Balance sheet
A balance sheet offers a snapshot of your company’s financial position at any given time. It demonstrates your business’s assets, liabilities, and equity giving you a concrete overview.
A balance sheet offers insight into a company’s financial stability, liquidity, and leverage helping the investors evaluate your business’s financial health.
Here are some important components in creating financial projections for a balance sheet:
| Activities | What it includes |
|---|---|
| Assets |
|
| Liabilities |
|
| Equity |
|
4. Break-even analysis
Break-even analysis determines your break-even point (BEP), where total revenue equals the total expenses of your business—a situation of no profit no loss.
Break-even analysis demonstrates how many units you must sell or the total sales you should make to reach a break-even point.
Here’s a quick formula to help you calculate the break-even point:

With these components covered, your business plan’s financial projections are equipped to provide investors and stakeholders with clear, actionable insights.
You can also refer to relevant samples of financial projections to get a more thorough overview of what to add.
Let’s now move to the next important question: How to create financial projections?
How to make financial projections for your startup
Let’s now walk you through the process of creating financial projections for a business plan:
1. Gather data
Although financial projections are assumptions, they must be backed with data and industrial insights. So naturally, as a first step, you should be gathering data.
What sort of data you may ask?
Well, existing businesses can gather historical financial data, such as balance sheets, cash flow statements, and annual income statements of the past years to base their projections for the future.
However, historical data isn’t enough to base future projections. Realistic and real-time market insights are also essential to get a more thorough overview of trends, market conditions, and the business’s future in the evolving marketplace.
For industrial insights, you can rely on sources like Statista, S&P Global, Gartner, and other high-impact organizations building research reports. Additionally, gather insights from competitor’s data to set benchmarks for your business.
2. Choose a forecasting approach
Now, how do you build your projections?
Well, there are two forecasting approaches that startups and existing businesses can consider:
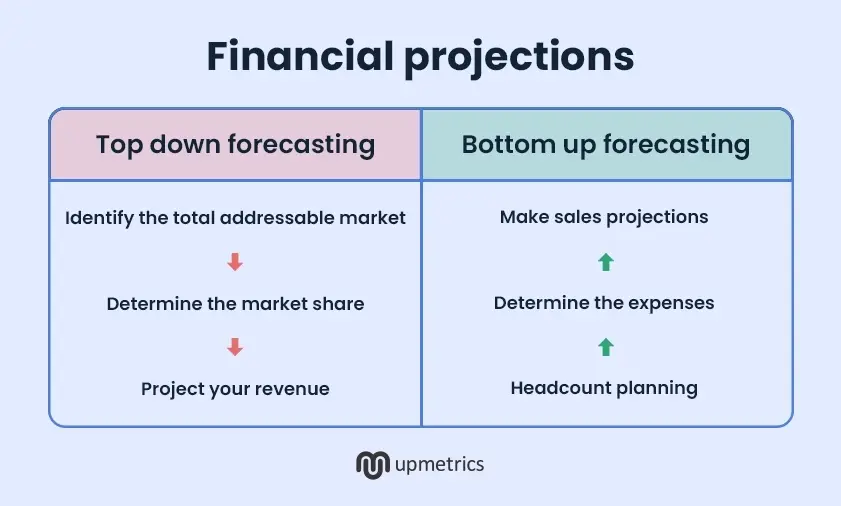
Top-down forecasting
The top-down approach begins with an industrial/market overview. From there you work your way down to project your total addressable market, estimated market share, and projected revenue.
This is the only known way for an emerging startup to build its revenue projections.
While practical, this approach has risks. Entrepreneurs often overestimate market share and underestimate challenges like customer acquisition or cash flow realities, leading to unrealistic projections.
Bottom-up forecasting
Here, you use your existing revenue and sales data to build projections for the future. However, it’s only efficient when an existing business has accurate internal data across all departments.
However, any errors in sales, revenue, or cost data can compound over time, making the projections unreliable.
3. Choose a forecasting tool
Building multi-year projections and reviewing them regularly is a time-intensive task. You simply can’t do that without an automated tool to guide you along.
As you choose a financial forecasting tool, here are a few things you should keep in mind:
- User-friendly interface: Choose a tool with an easier learning curve and navigation
- AI capabilities: AI functionalities to assist with different aspects of forecasting
- Integration capabilities: Should integrate seamlessly with accounting tools like Quickbooks and Xero
- Scenario analysis: Allows you to test multiple what-if scenarios essential for strategic decision-making
- Real-time updates: Syncs with real-time data for accurate forecasting
- Reporting and visualization: Clear, customizable reports and charts to communicate insights effectively
- Scalability: Ability to handle increasing data complexity as your business grows
- Budget: Choose a cost-effective tool that supports consistent forecasting in the budget
Prioritize the features that are important to you and select a tool that’s easier for you.
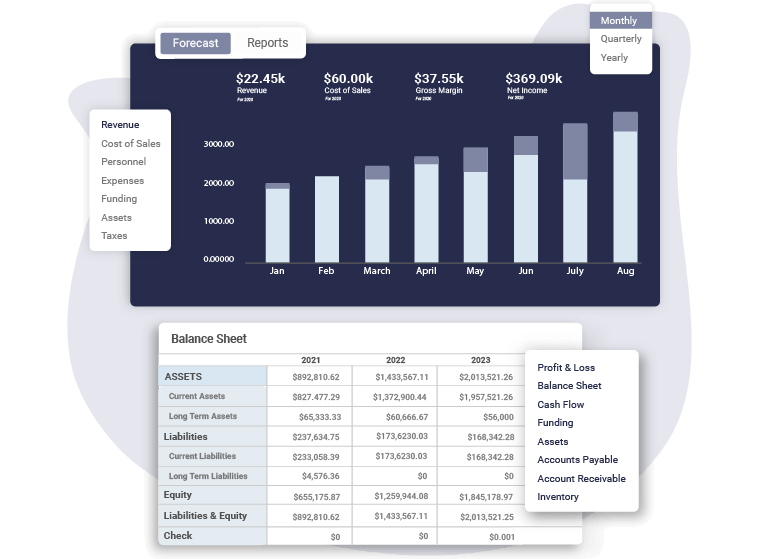
Since we are building financial projections for a business plan, ideally choose a business planning tool that supports forecasting, like Upmetrics.

Pro-tip
Create a Financial Plan with Upmetrics in no time
Enter your Financial Assumptions, and we’ll calculate your monthly/quarterly and yearly financial projections.
4. Headcount planning
Next up, you need a robust headcount plan before you make assumptions for expenses.
This is because salaries, benefits, and other forms of compensation can account for up to 35-40% of total business costs. These percentages can go as high as 75-80% for SaaS-based businesses.
So, are you planning to grow your team substantially over the coming years? If so, how many people are you planning to hire? Forecast the personnel count and the expenses you will be making every month on them.
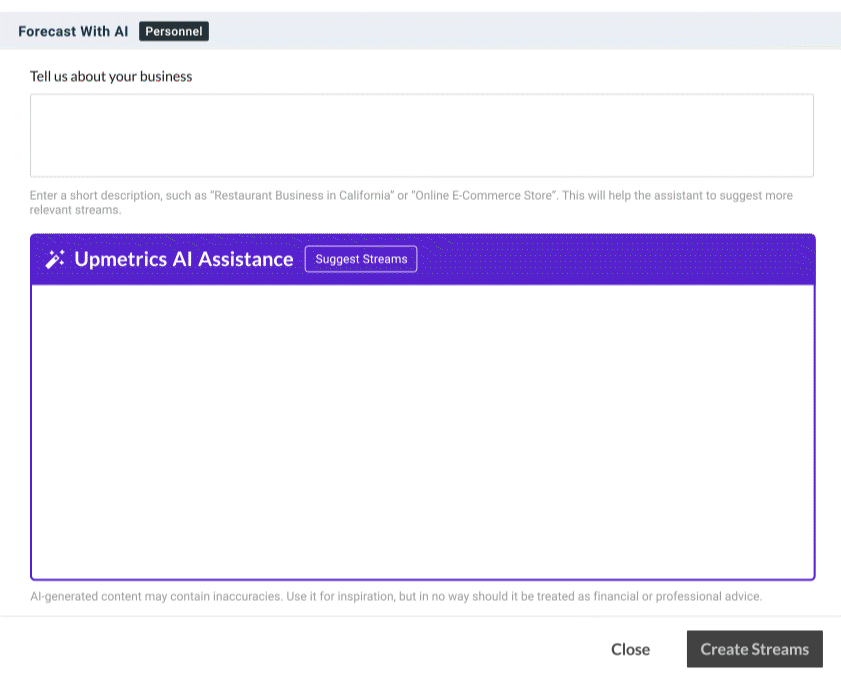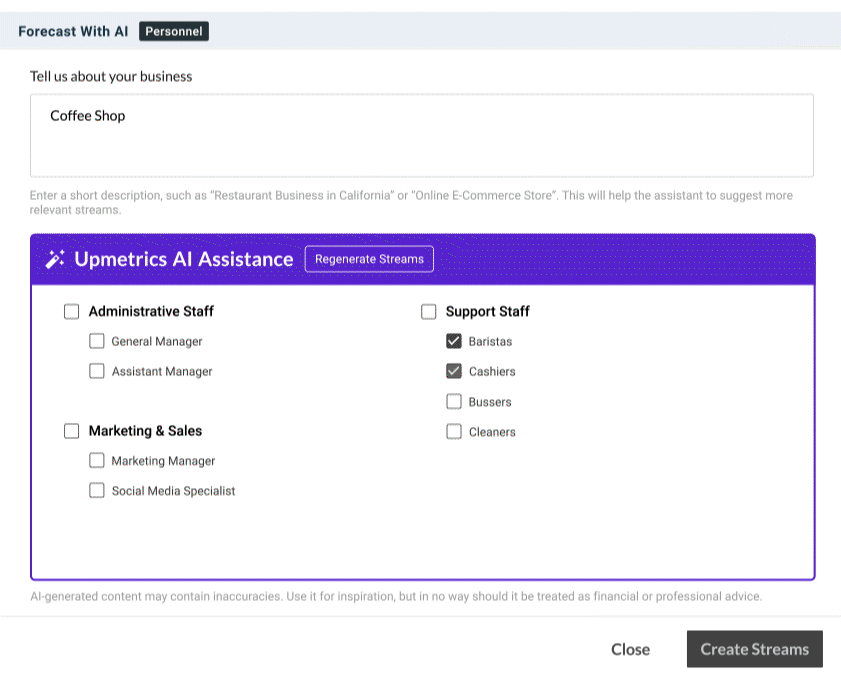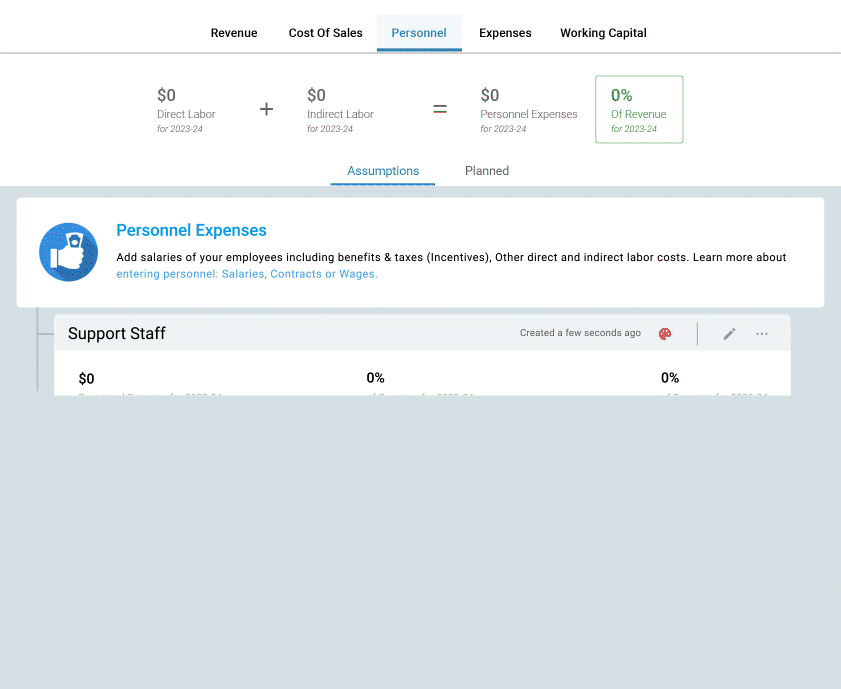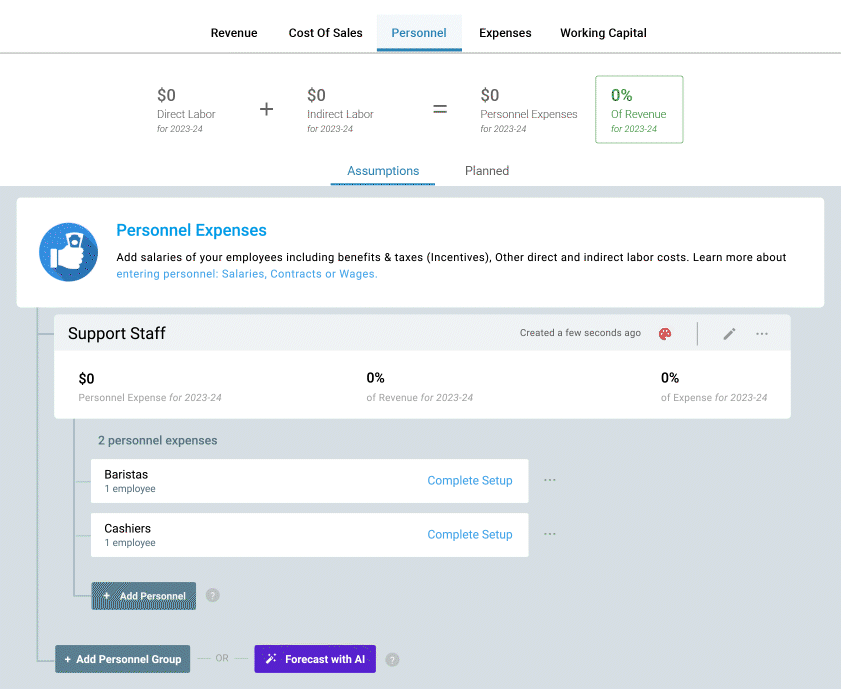
5. Forecast expenses
Systematically create a list of expenses you shall incur to produce the goods (COGS) and keep the business operational. This includes all sorts of operational, financial, administrative, marketing, and related expenses your business will incur.
New emerging businesses can begin by calculating their startup costs. This includes creating a table of fixed one-time expenses and recurring expenses for your business. Established businesses, however, can create expense streams by breaking down items in each department or product line.
As you forecast the expenses, ensure that you account for growth and market fluctuations to keep your expense forecasts accurate.
6. Forecast sales
Next up, estimate the sales volume for your business.
An accurate sales forecast will help manage cash flow, optimize resource allocation, and support strategic planning for future growth.
These projections typically rely on historical sales data, industry-wide benchmarks, and current economic trends. For startups or businesses without historical data, market research and competitor analysis become crucial.
Now, there are different methods of sales forecasting supporting different business models. However, at the fundamental level, all you need is reliable data and the ability to make logical and informed references from that data to make your sales assumptions relevant.
As you build the forecasts remember that Sales are constantly influenced by seasonal changes, downtimes, and consumer trends. You must account for such changes to avoid any major surprises in the future.
7. Build financial scenarios
Your financial projections are nothing but the set of your best assumptions. However, despite all the data and careful planning, unplanned situations may arise. It’s important to account for such situations in your financial forecasts.
Build a financial model for different progressive and aggressive situations. Accounting for a worst-case scenario includes situations, like disruptions in the supply chain, untimely resignations, hiccups in product development, regulatory shifts, etc.
Create financial statements reflecting these changes and add them along with your forecasts.
8. Build your financial projections
Now that you have your expenses, sales, and revenue, pull this information together and create your key financial statements.
You may use a business plan financial projections template or automate the process using ERP (enterprise resource planning), accounting, and financial forecasting tools like Upmetrics.
You can go the manual way, however, it’s neither productive nor feasible given the volume of data you would be trading with. Choose a system that integrates with your accounting system and pull together your financial statements, i.e. projected cash flow statement, projected income statement, and projected balance sheet.
And, that’s pretty much how you make financial projections for a business plan.
Say goodbye to old-school Excel and spreadsheets
Make realistic financial projections in minutes!

Download the startup financial projections template
Want to get a headstart on your financial projections? Download our startup financial projection template and use it to generate 3 key financial statements, i.e. balance sheet, income statement, and cash flow statement for your projections. Simply fill in your assumptions in the required fields and get your financial statements ready.
Start projecting financials using Upmetrics
With that, we’ve equipped you with all the knowledge you need to understand and make financial projections.
However, knowledge alone wouldn’t help you build projections for your business plan. You need a reliable and easy-to-use tool to ease financial planning.
That’s where Upmetrics’s financial forecasting tool steps in. With it, you can
- Utilize AI-powered suggestions for revenue and expenses.
- Test multiple scenarios to plan for uncertainties
- Build automated forecasts tailored to your business needs
- Generate detailed visual reports to communicate insights effectively
- Forecast for up to 7 years, ensuring long-term financial planning
- Integrate your existing data from Quickbooks and Xero
So what’s stopping you? Add accurate financial projections to your financial plan and present them to the investors.


