As we all know, the demand for foreign goods has increased all over the world more than it’s ever been. And this will offer you a golden opportunity to start your own import-export business!
Whether you’re importing tropical fruits and vegetables, exporting spices and clothes, or even machinery, all you need is passion to drive your business.
Yet, you might have thousands of thoughts or ideas swirling in your mind, including how to manage funding resources for navigating the ins and outs of the global marketplaces.
Surprisingly, the best way to answer all these questions is to write a comprehensive business plan. Here is our import-export business plan template, which will surely help you write your business plan in no time.
Before you start writing your business plan for your new import-export business, let’s go through some basic details.
What is an Import-export business plan?
An import-export business plan is a professional document that outlines the objectives, strategies, operational details, and financial projections of a business engaged in global trade.
It serves as a detailed blueprint, providing a clear picture of market opportunity and helping you navigate the potential challenges of cross-border business.
Why do you need an Import-export business plan?
A well-written business plan is a foundation for planning, managing, and developing an import-export business. It provides a roadmap for your business venture.
An actionable plan helps you summarize your business idea, strategies, goals, and financial projections if you’re seeking to raise funding from investors or banks.
Additionally, a professional business plan helps you comprehend the facts, constraints, and implementation schedules around international efforts.
Now, without further ado; let’s move forward to create a winning business plan:
How to Write an Import-Export Business Plan?
1. Executive Summary
An executive summary is the first section of the business plan, usually written at the last when the whole plan is ready.
It provides a high-level overview of the import-export business plan. It summarizes the key points, from business concept to financial outlook, for a quick understanding of your business.
The executive summary must be clear, concise, yet engaging as it is an introductory part of the plan and attracts readers to delve further into it.
You may start this section with a brief introduction to the import-export company, including the business name and the type of business you are operating.
After that, highlight the following key components:
- Company’s core objectives
- Mission-vision statements
- Market Opportunity
- Products and services offered
- Leadership team
- Financial statements
Note that potential investors or readers will surely go through this chapter before making a judgment, so make every word count.
Say goodbye to boring templates
Build your business plan faster and easier with AI
Plans starting from $14/month

2. Company Overview
The company overview section provides a detailed description of your business. It includes your business concept, ownership structure, history, future goals, and other business-related points.
Since you’ll give a brief business description in the executive summary, this chapter will expand on it, providing an in-depth understanding of your import-export business.
You may start by describing the fundamental details of your company, including name, concept, owners, legal structure, type of business you own, and what you’re importing or exporting.
For instance, you might own one of the several types of import-export companies: export trading company, export management company, or import-export merchant(agent)
Next, provide the start-up summary or background on your business. You may also highlight future business goals and milestones you have achieved.
For example, you may refer to the Walter’s long-term objectives:
Walter’s Long-term Objectives
The three-year goals for Walter Imports are the following:
- Achieve break-even by year 2.
- Retain our long-term contracts with local import shops in Leavenworth, WA, through excellent customer service.
- Become the premier importer of German and Scandinavian specialty products in Leavenworth, and become the prime exporter of apples and other produce for the farmers of the PCC Farmland Fund initiative.
Don’t forget to outline business insurance coverage, necessary licenses, and customs rules and regulations in both import and export countries.
3. Industry Analysis
Industry analysis is a study of your external business environment, providing a complete overview of the industry you serve and its dynamics.
This section helps potential investors and readers understand your market size, growth projections, target customers, and evolving trends. So make sure that you play your cards correctly.
You may conduct thorough market research to identify the feasible market for your imported or exported products. Also, analyze the market conditions, target market demands, and legal considerations.
Try to answer the following questions while conducting a market analysis:
- What is the current market size of the import-export industry?
- Is the market growing or falling in the USA?
- What are the major trends in the global market?
- Who are the top players in the import-export business?
- Which factors affect your business most?
- Who are your target customers you serve and/or expect to serve?
- What are the ideal customers’ buying patterns and needs?
Have a look at Walter’s ideal customer preferences:

In short, Industry analysis section will educate you about the market and help you develop business strategies according to the market trends.
4. Competitive Analysis
Competitive analysis is crucial to identify key competitors in the international trading market. It will help you determine your unique selling propositions and market positioning.
You may start this section by listing out all your direct and indirect competitors along with their strengths, weaknesses, and market share.
Most likely, your direct competitors or import-export businesses near your location can be more threatening to your company.
So, try to assess their specific products and services, pricing strategy, and type of customers they serve. If possible, ask for feedback directly from their customers and get valuable insights into their preferences.
Doing so will help you demonstrate your competitive advantage and USPs that set your company apart from other businesses.
5. Products and Service Offerings
This section provides a detailed description of the products & services you intend to offer and highlights the scope of your offerings, pricing plans, and more.
Since it’s your opportunity to narrate about the tangible goods or services you will be dealing with, you need to make your offerings exceptional to attract potential investors or partners.
Start writing this section with a detailed breakdown of the products you will be importing or exporting. It could be raw materials, consumer goods, machinery, raw materials, or specialized products.
You may outline the product description along with its pricing, specifications, variants, and any special features.
Here is an example of product offerings written with the help of Upmetrics AI-writing assistant:
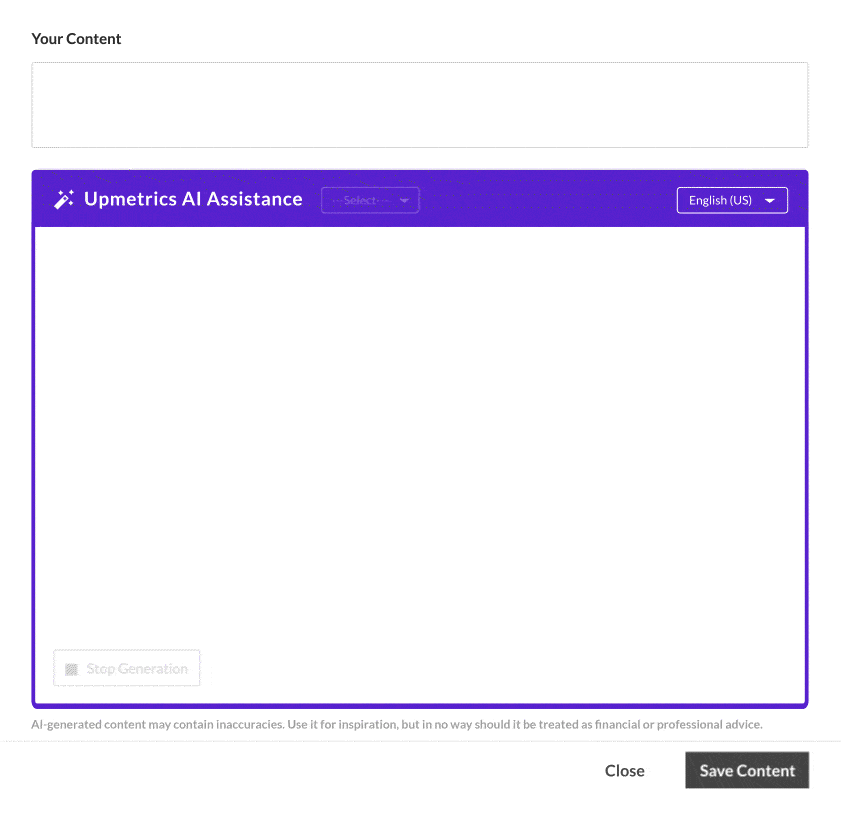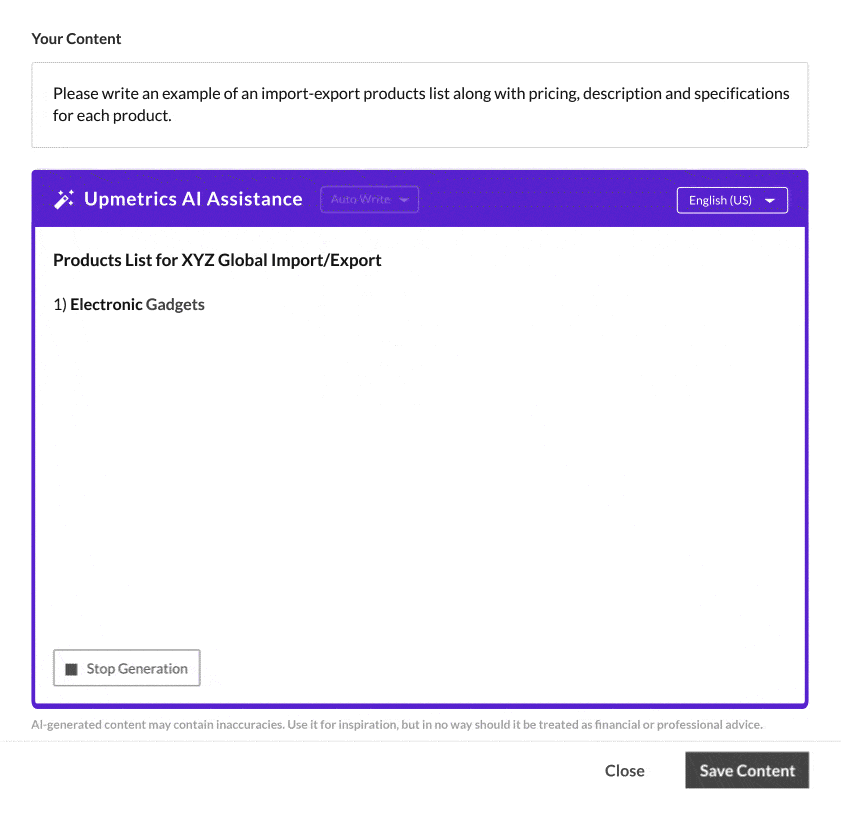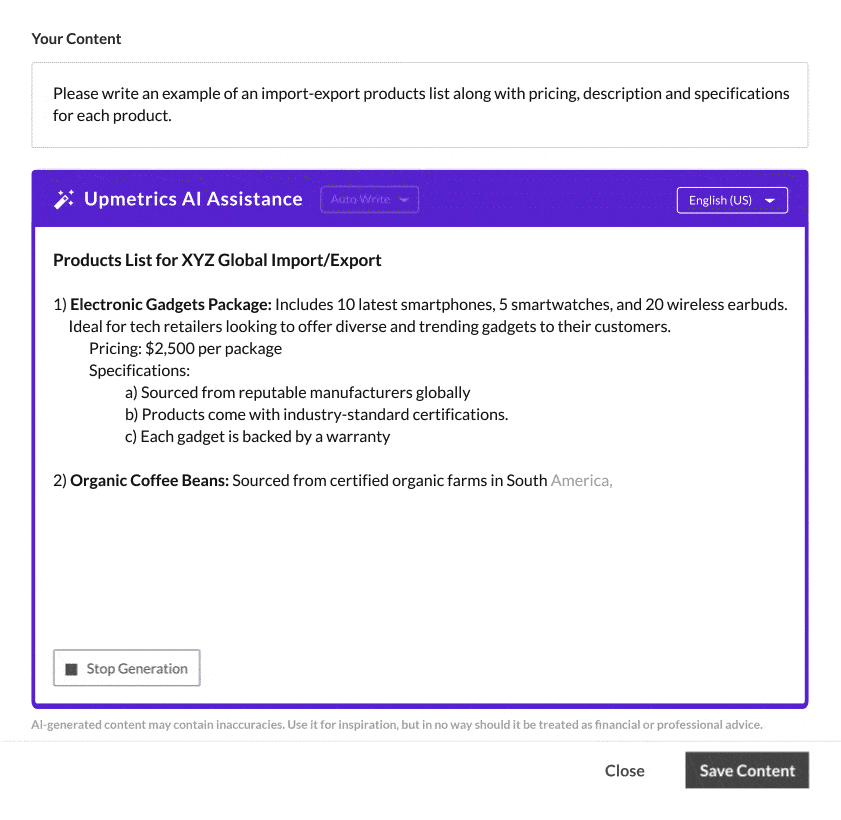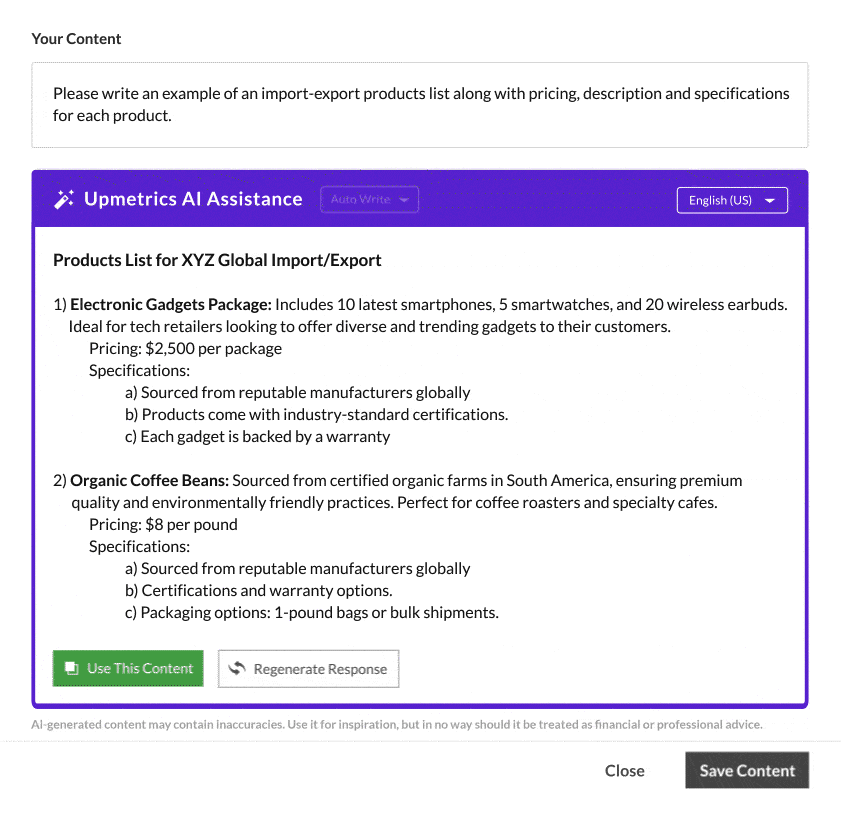
If your business encloses service provision in the import-export process, you may specify these services, which could be logistics, quality assurance, custom clearance, or any value-based services.
6. Marketing Plan
The marketing plan provides an in-depth understanding of sales strategies and promotional techniques you will use to acquire new customers and retain existing ones.
This section helps you streamline your marketing efforts and create effective advertising campaigns to reach your target market while keeping track of the estimated budget and maximizing return on investment.
You might consider including the below strategies in your plan:
Brand Image and Positioning
Create a strong brand image and position your imported/exported products strategically. Share the value of your products and emphasize superior quality or eco-friendly practices.
Unique Value Proposition(UVP)
Describe a compelling unique value proposition and define what sets you apart from the competition. Highlight a few elements, such as product quality, ethical practices, sourcing transparency, etc.
Digital Marketing Channels
Establish a professional website, leverage social media platforms, and invest in advertising campaigns to reach the target audience. Showcase your product range or updates and share valuable content related to products or global trade insights. It will enhance your online presence.
Partnerships
Try to build healthy relationships with distributors, retailers, and local businesses. Participate in networking events, trade exhibitions, and online forums.
Customer Retention Strategies
Develop strategies to foster loyalty among customers. Implement loyalty programs, after-sales support, personalized communication, word-of-mouth referrals, or discounts for repeat clients.
7. Management Team
The management team section introduces the business owners and key managers, along with their roles & responsibilities, educational background, work experience, and compensation plan.
A powerful management team helps potential investors or readers to be confident about your import-export business’s idea and vision.
You may start writing with an introduction, highlighting the crucial role of leadership in the ultimate success of your business.
Describe owners and key members of your management staff, including senior management and other employees. Mention their roles and responsibilities, qualifications, and experience.
Also, add an organizational chart that represents the reporting structure and explains how decisions will be made.
You may refer to the below example of an organizational structure crafted using Upmetrics:
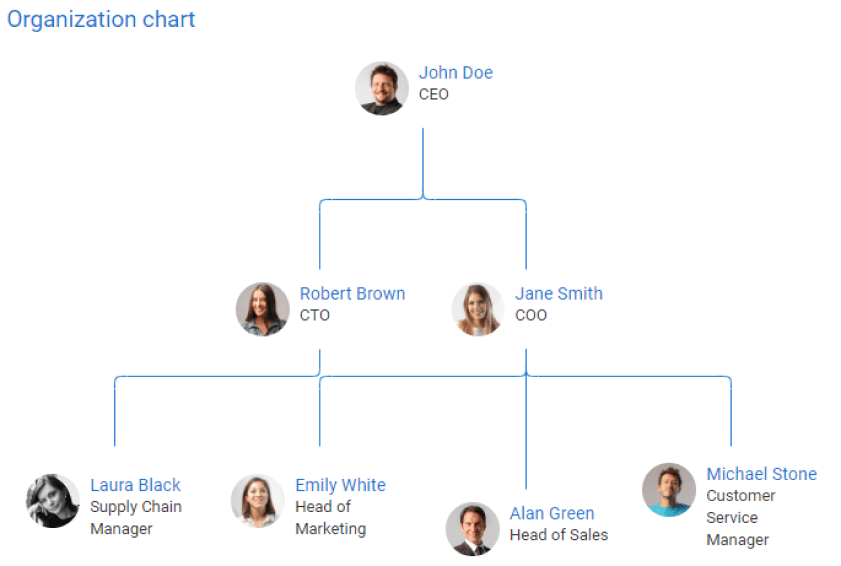
Next, outline your compensation plan which includes owners’ and key members’ earnings, bonuses, and benefits.
8. Operations Plan
The operations plan summarizes the day-to-day processes involved in the import-export company. These activities are centered on achieving the business goals and objectives described in the earlier sections.
This section helps you define your team’s responsibilities, daily tasks, and short-term goals you need to accomplish, keeping track of your long-term objectives.
For your import-export business, you may explain logistics, inventory management, distribution & warehousing, customs brokerage, and shipping & freight forwarding.
You may also highlight the quality control measures and the technology you use for order processing or real-time tracking.
Don’t forget to develop a risk mitigation strategy for probable disruptions in the supply chain, including natural disasters, global crises, or political fluctuations.
9. Financial Plan
A financial plan is the most crucial and demanding aspect of business plans.
Financial projections can be a deciding factor when it comes to persuading potential investors or banks to invest or lend money for your import-export business.
This section details all the financial information of your business, such as startup costs, cash flow & revenue streams, projected profits, and strategies to achieve financial goals.
You must include below key components and financial statements while creating a financial plan:
- Income statement
- Balance sheet
- Cash flow projections
- Capital requirements
- Operating costs
- Break-even point
- Business ratios
- Tax considerations
From the above financial forecasts, you can evaluate the funding resources for your import-export business, including bank loans, crowdfunding, investors, or personal savings.
Download Import-Export Business Plan Template
Need help writing your import-export business plan from scratch? Here you go; download our free import-export business plan pdf and get started.
It’s a modern, investment-ready business plan template specifically designed for your import-export business. Use this sample business plan as a guide for writing your own.
The Quickest Way to turn a Business Idea into a Business Plan
Fill-in-the-blanks and automatic financials make it easy.
Start Preparing Your Business Plan with Upmetrics
There’s no doubt—creating business plans that draw investors in can be a very daunting task, but it becomes a lot smoother with the use of Upmetrics!
Whether you’re starting a new business or looking to expand one, Upmetrics offers valuable resources, such as step-by-step guides, 400+ sample business plans, and AI assistance that will serve you perfectly.
Also, our financial forecasting tool will help you create realistic financial forecasts for 3 or more years if you’re not adept with finances.
So, what are you waiting for? Start planning now!




